当前面初始化完成的时候,zebra客户端线程(zebra_apic)静静等待客户端的消息,zebra dplane也急不可待了。
本次我们以BGP 为例,当BGP 根据自己的规则优选路由后,就会发给zebra,在函数bgp_process_main_one里面,把路由发布出去后,就会执行fib update动作,调用bgp_zebra_announce函数发布路由到zebra里面。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| /* FIB update. */
if (bgp_fibupd_safi(safi) && (bgp->inst_type != BGP_INSTANCE_TYPE_VIEW)
&& !bgp_option_check(BGP_OPT_NO_FIB)) {
if (new_select && new_select->type == ZEBRA_ROUTE_BGP
&& (new_select->sub_type == BGP_ROUTE_NORMAL
|| new_select->sub_type == BGP_ROUTE_AGGREGATE
|| new_select->sub_type == BGP_ROUTE_IMPORTED)) {
/* if this is an evpn imported type-5 prefix,
* we need to withdraw the route first to clear
* the nh neigh and the RMAC entry.
*/
if (old_select &&
is_route_parent_evpn(old_select))
bgp_zebra_withdraw(p, old_select, bgp, safi);
bgp_zebra_announce(dest, p, new_select, bgp, afi, safi);
} else {
/* Withdraw the route from the kernel. */
if (old_select && old_select->type == ZEBRA_ROUTE_BGP
&& (old_select->sub_type == BGP_ROUTE_NORMAL
|| old_select->sub_type == BGP_ROUTE_AGGREGATE
|| old_select->sub_type == BGP_ROUTE_IMPORTED))
bgp_zebra_withdraw(p, old_select, bgp, safi);
}
}
|
他们之间通过struct zapi_route 消息通信
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| /*
* Some of these data structures do not map easily to
* a actual data structure size giving different compilers
* and systems. For those data structures we need
* to use the smallest available stream_getX/putX functions
* to encode/decode.
*/
struct zapi_route {
uint8_t type;
unsigned short instance;
/* If you add flags, update zclient_dump_route_flags */
uint32_t flags;
/* The older XXX_MESSAGE flags live here */
uint32_t message;
/*
* This is an enum but we are going to treat it as a uint8_t
* for purpose of encoding/decoding
*/
safi_t safi;
struct prefix prefix;
struct prefix_ipv6 src_prefix;
uint16_t nexthop_num;
struct zapi_nexthop nexthops[MULTIPATH_NUM];
/* Support backup routes for IP FRR, TI-LFA, traffic engineering */
uint16_t backup_nexthop_num;
struct zapi_nexthop backup_nexthops[MULTIPATH_NUM];
uint32_t nhgid;
uint8_t distance;
uint32_t metric;
route_tag_t tag;
uint32_t mtu;
vrf_id_t vrf_id;
uint32_t tableid;
/* SR-TE color (used for nexthop updates only). */
uint32_t srte_color;
|
首先填充消息内容,最后调用zclient_route_send 发送到zebra进程处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| /* Make Zebra API structure. */
api.vrf_id = bgp->vrf_id;
api.type = ZEBRA_ROUTE_BGP;
api.safi = safi;
api.prefix = *p;
SET_FLAG(api.message, ZAPI_MESSAGE_NEXTHOP);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| if (CHECK_FLAG(api.flags, ZEBRA_FLAG_ALLOW_RECURSION))
recursion_flag = 1;
zlog_debug("%s: %pFX: announcing to zebra (recursion %sset)",
__func__, p, (recursion_flag ? "" : "NOT "));
}
zclient_route_send(is_add ? ZEBRA_ROUTE_ADD : ZEBRA_ROUTE_DELETE,
zclient, &api);
}
|
按照前面初始化阶段的分析,我们知道zebra为BGP创建的zebra_apic线程会被唤醒,执行fd可读的事件回调函数zserv_read。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| static void zserv_client_event(struct zserv *client,
enum zserv_client_event event)
{
switch (event) {
case ZSERV_CLIENT_READ:
event_add_read(client->pthread->master, zserv_read, client,
client->sock, &client->t_read);
break;
case ZSERV_CLIENT_WRITE:
event_add_write(client->pthread->master, zserv_write, client,
client->sock, &client->t_write);
break;
}
}
|
本次我们先借助zserv_read来看下sock读取字节流的报文的处理方法,然后在继续讨论路由的处理。
- 先读取头部
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| /* Read length and command (if we don't have it already). */
if (already < ZEBRA_HEADER_SIZE) {
nb = stream_read_try(client->ibuf_work, sock,
ZEBRA_HEADER_SIZE - already);
if ((nb == 0 || nb == -1)) {
if (IS_ZEBRA_DEBUG_EVENT)
zlog_debug("connection closed socket [%d]",
sock);
goto zread_fail;
}
if (nb != (ssize_t)(ZEBRA_HEADER_SIZE - already)) {
/* Try again later. */
break;
}
already = ZEBRA_HEADER_SIZE;
}
|
- 解析头部,获取头部后面的数据区长度
1
2
3
4
5
| /* Reset to read from the beginning of the incoming packet. */
stream_set_getp(client->ibuf_work, 0);
/* Fetch header values */
hdrvalid = zapi_parse_header(client->ibuf_work, &hdr);
|
- 根据头部里面的数据区长度,获取数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| /* Read rest of data. */
if (already < hdr.length) {
nb = stream_read_try(client->ibuf_work, sock,
hdr.length - already);
if ((nb == 0 || nb == -1)) {
if (IS_ZEBRA_DEBUG_EVENT)
zlog_debug(
"connection closed [%d] when reading zebra data",
sock);
goto zread_fail;
}
if (nb != (ssize_t)(hdr.length - already)) {
/* Try again later. */
break;
}
}
|
获取完所有的消息后,又把消息添加事件到zebra主线程继续处理?为啥这么处理了?zebra_apic线程就只读取下消息,然后所有的消息给主线程处理?减少锁?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| void zserv_event(struct zserv *client, enum zserv_event event)
{
switch (event) {
case ZSERV_ACCEPT:
event_add_read(zrouter.master, zserv_accept, NULL, zsock, NULL);
break;
case ZSERV_PROCESS_MESSAGES:
event_add_event(zrouter.master, zserv_process_messages, client,
0, &client->t_process);
break;
case ZSERV_HANDLE_CLIENT_FAIL:
event_add_event(zrouter.master, zserv_handle_client_fail,
client, 0, &client->t_cleanup);
}
}
|
我们先看看zserv_process_messages函数的注释,然后继续跟踪消息的处理:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| /*
* Read and process messages from a client.
*
* This task runs on the main pthread. It is scheduled by client pthreads when
* they have new messages available on their input queues. The client is passed
* as the task argument.
*
* Each message is popped off the client's input queue and the action associated
* with the message is executed. This proceeds until there are no more messages,
* an error occurs, or the processing limit is reached.
*
* The client's I/O thread can push at most zrouter.packets_to_process messages
* onto the input buffer before notifying us there are packets to read. As long
* as we always process zrouter.packets_to_process messages here, then we can
* rely on the read thread to handle queuing this task enough times to process
* everything on the input queue.
*/
static void zserv_process_messages(struct event *thread)
{
struct zserv *client = EVENT_ARG(thread);
struct stream *msg;
struct stream_fifo *cache = stream_fifo_new();
uint32_t p2p = zrouter.packets_to_process;
bool need_resched = false;
frr_with_mutex (&client->ibuf_mtx) {
uint32_t i;
for (i = 0; i < p2p && stream_fifo_head(client->ibuf_fifo);
++i) {
msg = stream_fifo_pop(client->ibuf_fifo);
stream_fifo_push(cache, msg);
}
/* Need to reschedule processing work if there are still
* packets in the fifo.
*/
if (stream_fifo_head(client->ibuf_fifo))
need_resched = true;
}
/* Process the batch of messages */
if (stream_fifo_head(cache))
zserv_handle_commands(client, cache);
stream_fifo_free(cache);
/* Reschedule ourselves if necessary */
if (need_resched)
zserv_event(client, ZSERV_PROCESS_MESSAGES);
}
|
先从client的ibuf里面出队报文,然后缓存起来,然后遍历缓存,每个消息调用zserv_handle_commands来实现函数调转,路由添加的cmd是ZEBRA_ROUTE_ADD,对应执行函数是zread_route_add,此函数继续解析处理路由消息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| void (*const zserv_handlers[])(ZAPI_HANDLER_ARGS) = {
[ZEBRA_ROUTER_ID_ADD] = zread_router_id_add,
[ZEBRA_ROUTER_ID_DELETE] = zread_router_id_delete,
[ZEBRA_INTERFACE_ADD] = zread_interface_add,
[ZEBRA_INTERFACE_DELETE] = zread_interface_delete,
[ZEBRA_INTERFACE_SET_PROTODOWN] = zread_interface_set_protodown,
[ZEBRA_ROUTE_ADD] = zread_route_add,
[ZEBRA_ROUTE_DELETE] = zread_route_del,
|
使用zapi_route_decode解析路由消息的msg,获取前缀、nexthop等各种信息,还原struct zapi_route消息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| static void zread_route_add(ZAPI_HANDLER_ARGS)
{
struct stream *s;
struct zapi_route api;
afi_t afi;
struct prefix_ipv6 *src_p = NULL;
struct route_entry *re;
struct nexthop_group *ng = NULL;
struct nhg_backup_info *bnhg = NULL;
int ret;
vrf_id_t vrf_id;
struct nhg_hash_entry nhe, *n = NULL;
s = msg;
if (zapi_route_decode(s, &api) < 0) {
if (IS_ZEBRA_DEBUG_RECV)
zlog_debug("%s: Unable to decode zapi_route sent",
__func__);
return;
}
|
生成一个新的route entry然后填充里面的各种信息,这里我们先认识下zebra里面最重要的路由的节点的数据结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
| struct route_entry {
/* Link list. */
struct re_list_item next;
/* Nexthop group, shared/refcounted, based on the nexthop(s)
* provided by the owner of the route
*/
struct nhg_hash_entry *nhe;
/* Nexthop group from FIB (optional), reflecting what is actually
* installed in the FIB if that differs. The 'backup' group is used
* when backup nexthops are present in the route's nhg.
*/
struct nexthop_group fib_ng;
struct nexthop_group fib_backup_ng;
/* Nexthop group hash entry IDs. The "installed" id is the id
* used in linux/netlink, if available.
*/
uint32_t nhe_id;
uint32_t nhe_installed_id;
/* Tag */
route_tag_t tag;
/* Uptime. */
time_t uptime;
/* Type of this route. */
int type;
/* VRF identifier. */
vrf_id_t vrf_id;
/* Which routing table */
uint32_t table;
/* Metric */
uint32_t metric;
/* MTU */
uint32_t mtu;
uint32_t nexthop_mtu;
/* Flags of this route.
* This flag's definition is in lib/zebra.h ZEBRA_FLAG_* and is exposed
* to clients via Zserv
*/
uint32_t flags;
/* RIB internal status */
uint32_t status;
#define ROUTE_ENTRY_REMOVED 0x1
/* The Route Entry has changed */
#define ROUTE_ENTRY_CHANGED 0x2
/* The Label has changed on the Route entry */
#define ROUTE_ENTRY_LABELS_CHANGED 0x4
/* Route is queued for Installation into the Data Plane */
#define ROUTE_ENTRY_QUEUED 0x8
/* Route is installed into the Data Plane */
#define ROUTE_ENTRY_INSTALLED 0x10
/* Route has Failed installation into the Data Plane in some manner */
#define ROUTE_ENTRY_FAILED 0x20
/* Route has a 'fib' set of nexthops, probably because the installed set
* differs from the rib/normal set of nexthops.
*/
#define ROUTE_ENTRY_USE_FIB_NHG 0x40
/*
* Route entries that are going to the dplane for a Route Replace
* let's note the fact that this is happening. This will
* be useful when zebra is determing if a route can be
* used for nexthops
*/
#define ROUTE_ENTRY_ROUTE_REPLACING 0x80
/* Sequence value incremented for each dataplane operation */
uint32_t dplane_sequence;
/* Source protocol instance */
uint16_t instance;
/* Distance. */
uint8_t distance;
struct re_opaque *opaque;
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| /* Allocate new route. */
re = zebra_rib_route_entry_new(
vrf_id, api.type, api.instance, api.flags, api.nhgid,
api.tableid ? api.tableid : zvrf->table_id, api.metric, api.mtu,
api.distance, api.tag);
if (!CHECK_FLAG(api.message, ZAPI_MESSAGE_NHG)
&& (!CHECK_FLAG(api.message, ZAPI_MESSAGE_NEXTHOP)
|| api.nexthop_num == 0)) {
flog_warn(
EC_ZEBRA_RX_ROUTE_NO_NEXTHOPS,
"%s: received a route without nexthops for prefix %pFX from client %s",
__func__, &api.prefix,
zebra_route_string(client->proto));
XFREE(MTYPE_RE, re);
return;
}
|
然后处理nexthop的信息,遍历所有的nexthop生成struct nexthop数据结构,我们在来认识下这个重要的数据结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| /* Nexthop structure. */
struct nexthop {
struct nexthop *next;
struct nexthop *prev;
/*
* What vrf is this nexthop associated with?
*/
vrf_id_t vrf_id;
/* Interface index. */
ifindex_t ifindex;
enum nexthop_types_t type;
uint16_t flags;
|
生成nexthop信息,并加入route entry的nexthop链表里面,后续用于负载均衡
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| /*
* TBD should _all_ of the nexthop add operations use
* api_nh->vrf_id instead of re->vrf_id ? I only changed
* for cases NEXTHOP_TYPE_IPV4 and NEXTHOP_TYPE_IPV6.
*/
for (i = 0; i < nexthop_num; i++) {
struct nexthop *nexthop;
enum lsp_types_t label_type;
char nhbuf[NEXTHOP_STRLEN];
char labelbuf[MPLS_LABEL_STRLEN];
struct zapi_nexthop *api_nh = &nhops[i];
/* Convert zapi nexthop */
nexthop = nexthop_from_zapi(api_nh, flags, p, backup_nh_num);
if (!nexthop) {
flog_warn(
EC_ZEBRA_NEXTHOP_CREATION_FAILED,
"%s: Nexthops Specified: %u(%u) but we failed to properly create one",
__func__, nexthop_num, i);
if (ng)
nexthop_group_delete(&ng);
if (bnhg)
zebra_nhg_backup_free(&bnhg);
return false;
}
|
如果消息里面有mpls label的信息,也需要添加到nexthop里面
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| /* MPLS labels for BGP-LU or Segment Routing */
if (CHECK_FLAG(api_nh->flags, ZAPI_NEXTHOP_FLAG_LABEL)) {
STREAM_GETC(s, api_nh->label_num);
STREAM_GETC(s, api_nh->label_type);
if (api_nh->label_num > MPLS_MAX_LABELS) {
flog_err(
EC_LIB_ZAPI_ENCODE,
"%s: invalid number of MPLS labels (%u)",
__func__, api_nh->label_num);
return -1;
}
STREAM_GET(&api_nh->labels[0], s,
api_nh->label_num * sizeof(mpls_label_t));
}
|
Route entry填充好后,继续调用rib_add_multipath_nhe处理路由信息添加,让我们继续走下去细看。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| /*
* If we have an ID, this proto owns the NHG it sent along with the
* route, so we just send the ID into rib code with it.
*
* Havent figured out how to handle backup NHs with this yet, so lets
* keep that separate.
* Include backup info with the route. We use a temporary nhe here;
* if this is a new/unknown nhe, a new copy will be allocated
* and stored.
*/
if (!re->nhe_id) {
zebra_nhe_init(&nhe, afi, ng->nexthop);
nhe.nhg.nexthop = ng->nexthop;
nhe.backup_info = bnhg;
n = zebra_nhe_copy(&nhe, 0);
}
ret = rib_add_multipath_nhe(afi, api.safi, &api.prefix, src_p, re, n,
false);
/*
* rib_add_multipath_nhe only fails in a couple spots
* and in those spots we have not freed memory
*/
if (ret == -1) {
client->error_cnt++;
XFREE(MTYPE_RE_OPAQUE, re->opaque);
XFREE(MTYPE_RE, re);
}
|
process_subq_early_route_add 先查找本次的路由表的route_table,然后在table中根据前缀查找是否有相同的route_node表项,其中srcdest_rnode_get查找如果没有node,则会生成一个新的route_node,然后加入route_table的二叉树中,然后调用rib_addnode,添加route_entry表项。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| static void process_subq_early_route_add(struct zebra_early_route *ere)
{
struct route_entry *re = ere->re;
struct route_table *table;
struct nhg_hash_entry *nhe = NULL;
struct route_node *rn;
struct route_entry *same = NULL, *first_same = NULL;
int same_count = 0;
rib_dest_t *dest;
/* Lookup table. */
table = zebra_vrf_get_table_with_table_id(ere->afi, ere->safi,
re->vrf_id, re->table);
if (!table) {
early_route_memory_free(ere);
return;
}
|
process_subq_early_route_add 又引入了两个新的数据结构struct route_table和struct route_node,我们来看下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| /* Routing table top structure. */
struct route_table {
struct route_node *top;
struct rn_hash_node_head hash;
/*
* Delegate that performs certain functions for this table.
*/
route_table_delegate_t *delegate;
void (*cleanup)(struct route_table *, struct route_node *);
unsigned long count;
/*
* User data.
*/
void *info;
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| /* Each routing entry. */
struct route_node {
ROUTE_NODE_FIELDS
#define l_left link[0]
#define l_right link[1]
};
|
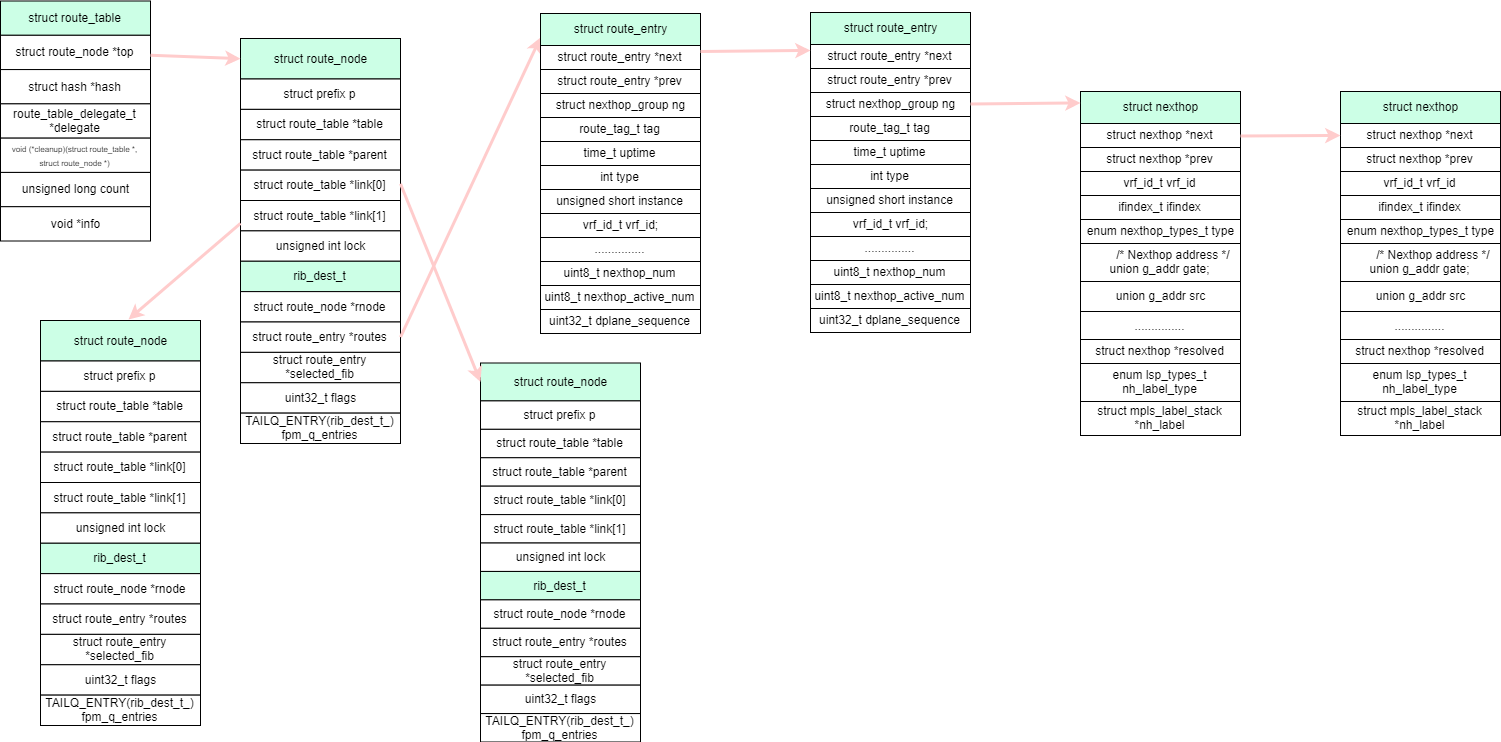
结合前面给出的nexthop,整个路由表项的处理就是由route_table \ route_node \ route_entry 组织而成的,route_table包含了一个二叉树结构来保存所有的路由前缀和下一跳路由表项,prefix结构保持了路由前缀的长度和值,用来做最长前缀匹配,那说好的mtire树呢? 好吧,我们不太可能把成千上万的路由表项塞给linux内核,够用就行。
整体的数据结构关系如下图所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| static void rib_addnode(struct route_node *rn,
struct route_entry *re, int process)
{
/* RE node has been un-removed before route-node is processed.
* route_node must hence already be on the queue for processing..
*/
if (CHECK_FLAG(re->status, ROUTE_ENTRY_REMOVED)) {
if (IS_ZEBRA_DEBUG_RIB)
rnode_debug(rn, re->vrf_id, "rn %p, un-removed re %p",
(void *)rn, (void *)re);
UNSET_FLAG(re->status, ROUTE_ENTRY_REMOVED);
return;
}
rib_link(rn, re, process);
}
|
rib_addnode 直接调用 rib_link 继续处理,首先会在 route_node 的info字段生成一个 rib_dest_t 的结构体,上面的图也已经画了出来,同时会把route_node里面的route_entry使用链表连接起来,表示同一个前缀的不同路由。
然后会判断是否有重分发的配置,如果bgp的路由重分发到ospf等,本次不分析,如果没有重分发,那么直接调用rib_queue_add入zebrad.mq work queue处理,当work queue调度处理的时候,会调回调函数meta_queue_process继续处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| /*
* Structure that represents a single destination (prefix).
*/
typedef struct rib_dest_t_ {
/*
* Back pointer to the route node for this destination. This helps
* us get to the prefix that this structure is for.
*/
struct route_node *rnode;
/*
* Doubly-linked list of routes for this prefix.
*/
struct re_list_head routes;
struct route_entry *selected_fib;
/*
* Flags, see below.
*/
uint32_t flags;
/*
* The list of nht prefixes that have ended up
* depending on this route node.
* After route processing is returned from
* the data plane we will run evaluate_rnh
* on these prefixes.
*/
struct rnh_list_head nht;
/*
* Linkage to put dest on the FPM processing queue.
*/
TAILQ_ENTRY(rib_dest_t_) fpm_q_entries;
} rib_dest_t;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| /* Add RE to head of the route node. */
static void rib_link(struct route_node *rn, struct route_entry *re, int process)
{
rib_dest_t *dest;
afi_t afi;
const char *rmap_name;
assert(re && rn);
dest = rib_dest_from_rnode(rn);
if (!dest) {
if (IS_ZEBRA_DEBUG_RIB_DETAILED)
rnode_debug(rn, re->vrf_id, "rn %p adding dest", rn);
dest = zebra_rib_create_dest(rn);
}
re_list_add_head(&dest->routes, re);
afi = (rn->p.family == AF_INET)
? AFI_IP
: (rn->p.family == AF_INET6) ? AFI_IP6 : AFI_MAX;
if (is_zebra_import_table_enabled(afi, re->vrf_id, re->table)) {
struct zebra_vrf *zvrf = zebra_vrf_lookup_by_id(re->vrf_id);
rmap_name = zebra_get_import_table_route_map(afi, re->table);
zebra_add_import_table_entry(zvrf, rn, re, rmap_name);
}
if (process)
rib_queue_add(rn);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| /* Add route_node to work queue and schedule processing */
int rib_queue_add(struct route_node *rn)
{
assert(rn);
/* Pointless to queue a route_node with no RIB entries to add or remove
*/
if (!rnode_to_ribs(rn)) {
zlog_debug("%s: called for route_node (%p, %u) with no ribs",
__func__, (void *)rn, route_node_get_lock_count(rn));
zlog_backtrace(LOG_DEBUG);
return -1;
}
return mq_add_handler(rn, rib_meta_queue_add);
}
|
前面可知,消息被enqueue了mq的work queue,当zebra的mq的work queue被调度的时候,meta_queue_process回调函数会被执行,for循环执行一个就退出,是为了实现subq的绝对优先级调度。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| /* Dispatch the meta queue by picking and processing the next node from
* a non-empty sub-queue with lowest priority. wq is equal to zebra->ribq and
* data is pointed to the meta queue structure.
*/
static wq_item_status meta_queue_process(struct work_queue *dummy, void *data)
{
struct meta_queue *mq = data;
unsigned i;
uint32_t queue_len, queue_limit;
/* Ensure there's room for more dataplane updates */
queue_limit = dplane_get_in_queue_limit();
queue_len = dplane_get_in_queue_len();
if (queue_len > queue_limit) {
if (IS_ZEBRA_DEBUG_RIB_DETAILED)
zlog_debug(
"rib queue: dplane queue len %u, limit %u, retrying",
queue_len, queue_limit);
/* Ensure that the meta-queue is actually enqueued */
if (work_queue_empty(zrouter.ribq))
work_queue_add(zrouter.ribq, zrouter.mq);
return WQ_QUEUE_BLOCKED;
}
for (i = 0; i < MQ_SIZE; i++)
if (process_subq(mq->subq[i], i)) {
mq->size--;
break;
}
return mq->size ? WQ_REQUEUE : WQ_SUCCESS;
}
|
process_subq 取出头结点的存放的struct route_node,然后直接调用rib_process继续处理route_node,其核心思想是遍历route_node的所有的route_entry根据规则选择最优的路由,然后使用这个最优的路由继续处理,rib_choose_best的原则在函数里面也说的很清楚。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| /* Check if 'alternate' RIB entry is better than 'current'. */
static struct route_entry *rib_choose_best(struct route_entry *current,
struct route_entry *alternate)
{
if (current == NULL)
return alternate;
/* filter route selection in following order:
* - connected beats other types
* - if both connected, loopback or vrf wins
* - lower distance beats higher
* - lower metric beats higher for equal distance
* - last, hence oldest, route wins tie break.
*/
/* Connected routes. Check to see if either are a vrf
* or loopback interface. If not, pick the last connected
* route of the set of lowest metric connected routes.
*/
if (alternate->type == ZEBRA_ROUTE_CONNECT) {
if (current->type != ZEBRA_ROUTE_CONNECT)
return alternate;
|
处理路由信息库的核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| /* Core function for processing routing information base. */
static void rib_process(struct route_node *rn)
{
struct route_entry *re;
struct route_entry *next;
struct route_entry *old_selected = NULL;
struct route_entry *new_selected = NULL;
struct route_entry *old_fib = NULL;
struct route_entry *new_fib = NULL;
struct route_entry *best = NULL;
rib_dest_t *dest;
struct zebra_vrf *zvrf = NULL;
struct vrf *vrf;
vrf_id_t vrf_id = VRF_UNKNOWN;
assert(rn);
dest = rib_dest_from_rnode(rn);
/*
* We have an enqueued node with nothing to process here
* let's just finish up and return;
*/
if (!dest)
return;
zvrf = rib_dest_vrf(dest);
vrf_id = zvrf_id(zvrf);
vrf = vrf_lookup_by_id(vrf_id);
/*
* we can have rn's that have a NULL info pointer
* (dest). As such let's not let the deref happen
* additionally we know RNODE_FOREACH_RE_SAFE
* will not iterate so we are ok.
*/
if (IS_ZEBRA_DEBUG_RIB_DETAILED) {
struct route_entry *re = re_list_first(&dest->routes);
zlog_debug("%s(%u:%u):%pRN: Processing rn %p",
VRF_LOGNAME(vrf), vrf_id, re->table, rn,
rn);
}
old_fib = dest->selected_fib;
RNODE_FOREACH_RE_SAFE (rn, re, next) {
|
本次我们以添加rib为例来分析,rib_process_add_fib主要完成4个事情,下面我们一个一个分析:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| static void rib_process_add_fib(struct zebra_vrf *zvrf, struct route_node *rn,
struct route_entry *new)
{
hook_call(rib_update, rn, "new route selected");
/* Update real nexthop. This may actually determine if nexthop is active
* or not. */
if (!nexthop_group_active_nexthop_num(&(new->nhe->nhg))) {
UNSET_FLAG(new->status, ROUTE_ENTRY_CHANGED);
return;
}
if (IS_ZEBRA_DEBUG_RIB)
zlog_debug("%s(%u:%u):%pRN: Adding route rn %p, re %p (%s)",
zvrf_name(zvrf), zvrf_id(zvrf), new->table, rn, rn,
new, zebra_route_string(new->type));
/* If labeled-unicast route, install transit LSP. */
if (zebra_rib_labeled_unicast(new))
zebra_mpls_lsp_install(zvrf, rn, new);
rib_install_kernel(rn, new, NULL);
UNSET_FLAG(new->status, ROUTE_ENTRY_CHANGED);
}
|
- hook_call,通知关心 rib_update 的订阅者
hook_call(rib_update, rn, "new route selected");
#define hook_call(hookname, ...) hook_call_##hookname(__VA_ARGS__)
宏展开后就是调用hook_call_ rib_update(rn, "new route selected")
而hook_call_ rib_update函数是在DEFINE_HOOK定义的,就是调用关心rib_update这个HOOK点的订阅者,rib_update定义如下:
1
2
3
| DEFINE_HOOK(rib_update, (struct route_node * rn, const char *reason),
(rn, reason));
DEFINE_HOOK(rib_shutdown, (struct route_node * rn), (rn));
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| /* use in source file - contains hook-related definitions.
*/
#define DEFINE_HOOK_INT(hookname, arglist, passlist, rev) \
struct hook _hook_##hookname = { \
.name = #hookname, .entries = NULL, .reverse = rev, \
}; \
static int hook_call_##hookname HOOK_VOIDIFY arglist \
{ \
int hooksum = 0; \
struct hookent *he = _hook_##hookname.entries; \
void *hookarg; \
union { \
void *voidptr; \
int(*fptr) HOOK_VOIDIFY arglist; \
int(*farg) HOOK_ADDDEF arglist; \
} hookp; \
for (; he; he = he->next) { \
hookarg = he->hookarg; \
hookp.voidptr = he->hookfn; \
if (!he->has_arg) \
hooksum += hookp.fptr passlist; \
else \
hooksum += hookp.farg HOOK_ADDARG passlist; \
} \
return hooksum; \
} \
MACRO_REQUIRE_SEMICOLON() /* end */
#define DEFINE_HOOK(hookname, arglist, passlist) \
DEFINE_HOOK_INT(hookname, arglist, passlist, false)
#define DEFINE_KOOH(hookname, arglist, passlist) \
DEFINE_HOOK_INT(hookname, arglist, passlist, true)
|
而rib_update订阅者的注册如下,目前有fpm, hook_register调用_hook_register函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| static int zebra_fpm_module_init(void)
{
hook_register(rib_update, zfpm_trigger_update);
hook_register(rib_shutdown, zfpm_trigger_remove);
hook_register(zebra_rmac_update, zfpm_trigger_rmac_update);
hook_register(frr_late_init, zfpm_init);
hook_register(frr_early_fini, zfpm_fini);
return 0;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| void _hook_register(struct hook *hook, struct hookent *stackent, void *funcptr,
void *arg, bool has_arg, struct frrmod_runtime *module,
const char *funcname, int priority)
{
struct hookent *he, **pos;
if (!stackent->ent_used)
he = stackent;
else {
he = XCALLOC(MTYPE_HOOK_ENTRY, sizeof(*he));
he->ent_on_heap = true;
}
he->ent_used = true;
he->hookfn = funcptr;
he->hookarg = arg;
he->has_arg = has_arg;
he->module = module;
he->fnname = funcname;
he->priority = priority;
for (pos = &hook->entries; *pos; pos = &(*pos)->next)
if (hook->reverse ? (*pos)->priority < priority
: (*pos)->priority >= priority)
break;
he->next = *pos;
*pos = he;
}
|
所以hook_call(rib_update, rn, “new route selected”)调用的是zfpm_trigger_update函数。
- 检查nexthop的active 其主要完成遍历re的所有的nexthop,然后调用
nexthop_active_check/ nexthop_active检查nexthop是否是active,根据nexthop填充prefix查找路由表,查看下一跳是否在路由表里面,如果是CONNECT路由,那么解析active成功,如果下一跳不是CONNECT的路由,同时还要处理路由递归的情况,把递归的路由存放在struct nexthop的resolved里面,此时的resolved里面存放的路由肯定是前面已经检查并active的路由,所以不并在递归继续查找了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| /* This function verifies reachability of one given nexthop, which can be
* numbered or unnumbered, IPv4 or IPv6. The result is unconditionally stored
* in nexthop->flags field. The nexthop->ifindex will be updated
* appropriately as well.
*
* An existing route map can turn an otherwise active nexthop into inactive,
* but not vice versa.
*
* The return value is the final value of 'ACTIVE' flag.
*/
static unsigned nexthop_active_check(struct route_node *rn,
struct route_entry *re,
struct nexthop *nexthop,
struct nhg_hash_entry *nhe)
{
route_map_result_t ret = RMAP_PERMITMATCH;
afi_t family;
const struct prefix *p, *src_p;
struct zebra_vrf *zvrf;
uint32_t mtu = 0;
vrf_id_t vrf_id;
srcdest_rnode_prefixes(rn, &p, &src_p);
if (rn->p.family == AF_INET)
family = AFI_IP;
else if (rn->p.family == AF_INET6)
family = AFI_IP6;
else
family = AF_UNSPEC;
if (IS_ZEBRA_DEBUG_NHG_DETAIL)
zlog_debug("%s: re %p, nexthop %pNHv", __func__, re, nexthop);
vrf_id = zvrf_id(rib_dest_vrf(rib_dest_from_rnode(rn)));
/*
* If this is a kernel route, then if the interface is *up* then
* by golly gee whiz it's a good route.
*/
if (re->type == ZEBRA_ROUTE_KERNEL || re->type == ZEBRA_ROUTE_SYSTEM) {
struct interface *ifp;
ifp = if_lookup_by_index(nexthop->ifindex, nexthop->vrf_id);
if (ifp && ifp->vrf->vrf_id == vrf_id && if_is_up(ifp)) {
SET_FLAG(nexthop->flags, NEXTHOP_FLAG_ACTIVE);
goto skip_check;
}
}
switch (nexthop->type) {
case NEXTHOP_TYPE_IFINDEX:
if (nexthop_active(nexthop, nhe, &rn->p, re->type, re->flags,
&mtu, vrf_id))
SET_FLAG(nexthop->flags, NEXTHOP_FLAG_ACTIVE);
else
UNSET_FLAG(nexthop->flags, NEXTHOP_FLAG_ACTIVE);
break;
|
- 下发LSP,MPLS的转发表
如果re是BGP的labeled unicast产生的,那么我们需要向内核下发LSP,MPLS的转发表,具体的下发过程,我们后面分析MPLS的时候,在继续分析
1
2
3
| /* If labeled-unicast route, install transit LSP. */
if (zebra_rib_labeled_unicast(new))
zebra_mpls_lsp_install(zvrf, rn, new);
|
- 向内核下发FIB表项
调用rib_install_kernel函数处理,直接调用dplane_route_add,入队数据平面的队列。
根据前面的初始化分析,我们知道:
zebra_dplane_init_internal初始化了kernel的数据平面的回调函数kernel_dplane_process_func
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| /*
* Register default kernel provider
*/
static void dplane_provider_init(void)
{
int ret;
ret = dplane_provider_register("Kernel",
DPLANE_PRIO_KERNEL,
DPLANE_PROV_FLAGS_DEFAULT, NULL,
kernel_dplane_process_func,
NULL,
NULL, NULL);
if (ret != AOK)
zlog_err("Unable to register kernel dplane provider: %d",
ret);
|
dplane_route_add调用dplane_route_enqueue把FIB消息入队,并添加事件唤醒dplan 线程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| /*
* Enqueue a route 'add' for the dataplane.
*/
enum zebra_dplane_result dplane_route_add(struct route_node *rn,
struct route_entry *re)
{
enum zebra_dplane_result ret = ZEBRA_DPLANE_REQUEST_FAILURE;
if (rn == NULL || re == NULL)
return ret;
ret = dplane_route_update_internal(rn, re, NULL,
DPLANE_OP_ROUTE_INSTALL);
return ret;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| /*
* Enqueue a new update,
* and ensure an event is active for the dataplane pthread.
*/
static int dplane_update_enqueue(struct zebra_dplane_ctx *ctx)
{
int ret = EINVAL;
uint32_t high, curr;
/* Enqueue for processing by the dataplane pthread */
DPLANE_LOCK();
{
dplane_ctx_list_add_tail(&zdplane_info.dg_update_list, ctx);
}
DPLANE_UNLOCK();
curr = atomic_fetch_add_explicit(
&(zdplane_info.dg_routes_queued),
1, memory_order_seq_cst);
curr++; /* We got the pre-incremented value */
/* Maybe update high-water counter also */
high = atomic_load_explicit(&zdplane_info.dg_routes_queued_max,
memory_order_seq_cst);
while (high < curr) {
if (atomic_compare_exchange_weak_explicit(
&zdplane_info.dg_routes_queued_max,
&high, curr,
memory_order_seq_cst,
memory_order_seq_cst))
break;
}
/* Ensure that an event for the dataplane thread is active */
ret = dplane_provider_work_ready();
return ret;
}
|
zebra_dplane_start创建了zebra dplane的线程, 线程的事件回调函数dplane_thread_loop,在这个函数里面会出队所有的消息,并调用注册的数据面的回调函数,本次路由的回调函数是kernel_dplane_process_func,然后调用kernel_route_update,继续调用netlink_route_multipath,构造路由的netlink消息,下发给内核,下发的路由会设置NEXTHOP_FLAG_FIB。
同时调用netlink_parse_info处理内核的处理结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| /*
* Update or delete a prefix from the kernel,
* using info from a dataplane context struct.
*/
enum zebra_dplane_result kernel_route_update(struct zebra_dplane_ctx *ctx)
{
enum zebra_dplane_result res = ZEBRA_DPLANE_REQUEST_SUCCESS;
uint32_t type, old_type;
if (dplane_ctx_get_src(ctx) != NULL) {
zlog_err("route add: IPv6 sourcedest routes unsupported!");
return ZEBRA_DPLANE_REQUEST_FAILURE;
}
type = dplane_ctx_get_type(ctx);
old_type = dplane_ctx_get_old_type(ctx);
frr_with_privs(&zserv_privs) {
if (dplane_ctx_get_op(ctx) == DPLANE_OP_ROUTE_DELETE) {
if (!RSYSTEM_ROUTE(type))
kernel_rtm(RTM_DELETE, dplane_ctx_get_dest(ctx),
dplane_ctx_get_ng(ctx),
dplane_ctx_get_metric(ctx));
} else if (dplane_ctx_get_op(ctx) == DPLANE_OP_ROUTE_INSTALL) {
if (!RSYSTEM_ROUTE(type))
kernel_rtm(RTM_ADD, dplane_ctx_get_dest(ctx),
dplane_ctx_get_ng(ctx),
dplane_ctx_get_metric(ctx));
} else if (dplane_ctx_get_op(ctx) == DPLANE_OP_ROUTE_UPDATE) {
/* Must do delete and add separately -
* no update available
*/
if (!RSYSTEM_ROUTE(old_type))
kernel_rtm(RTM_DELETE, dplane_ctx_get_dest(ctx),
dplane_ctx_get_old_ng(ctx),
dplane_ctx_get_old_metric(ctx));
if (!RSYSTEM_ROUTE(type))
kernel_rtm(RTM_ADD, dplane_ctx_get_dest(ctx),
dplane_ctx_get_ng(ctx),
dplane_ctx_get_metric(ctx));
} else {
zlog_err("Invalid routing socket update op %s (%u)",
dplane_op2str(dplane_ctx_get_op(ctx)),
dplane_ctx_get_op(ctx));
res = ZEBRA_DPLANE_REQUEST_FAILURE;
}
} /* Elevated privs */
return res;
}
|
把上面的分析的函数主要路径总结如下,细节只有慢慢去看:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| zebra_apic线程
zserv_read
zserV_event --> 发事件给ZEBRA的主线程
zebra线程
zserv_process_message
zserv_handle_commands
zread_route_add
rib_add_multipath
rib_addnode
meta_queue_process 处理队列上的消息
process subg
rib process
rib_process_add_fib 添加新的fib
hook_call(rib_update,rn, "new route selected"); --回调函数处理zfpm_trigger_update,通知FPM
rib_install_kernel 下发到内核
dplane route add
dpiane_route_enqueue 入队处理,异步给zebra_plane线程处理
zebra_plane线程
dplane_thread_loop
kernel_dplane_process_func(*prov->dp_fp)(prov)
kernel_dplane_route_update
kernel_route_update
netlink_route_multipath
netlink_talk_info
sendmsg(nl->sock,&msg,0)
netlink_parse_info
fpm客户端库处理
zfpm_trigger_update
TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&zfpm_g->dest_q, dest, fpm_q_entries); 任务调度
zfpm_write_cb
zfpm_build_updates
zfpm_encode_route
zfpm_netlink_encode_route
netlink_route_info_encode
write(zfpm_g->sock,streampnt(s),bytes_towrite);发送给服务端
|
本文参考
- BGP官方文档
- FRR BGP 协议分析