BGP协议建立起来后,后续的核心就是UPDATE路由,其关键的部分还是在路由的更新与撤销上面,这之间包含了繁杂的属性的处理过程。
我们知道,BGP发布路由时采用如下策略:
- 存在多条有效路由时,BGP Speaker只将最优路由发布给对等体。
- BGP Speaker从EBGP获得的路由会向它所有BGP对等体发布(包括EBGP对等体和IBGP对等体)。
- BGP Speaker从IBGP获得的路由不向它的IBGP对等体发布。
- BGP Speaker从IBGP获得的路由发布给它的EBGP对等体。
- 连接一旦建立,BGP Speaker将把自己所有BGP最优路由发布给新对等体。
我们先认识下BGP的 UPDATE消息,在展开代码的分析。
Update消息
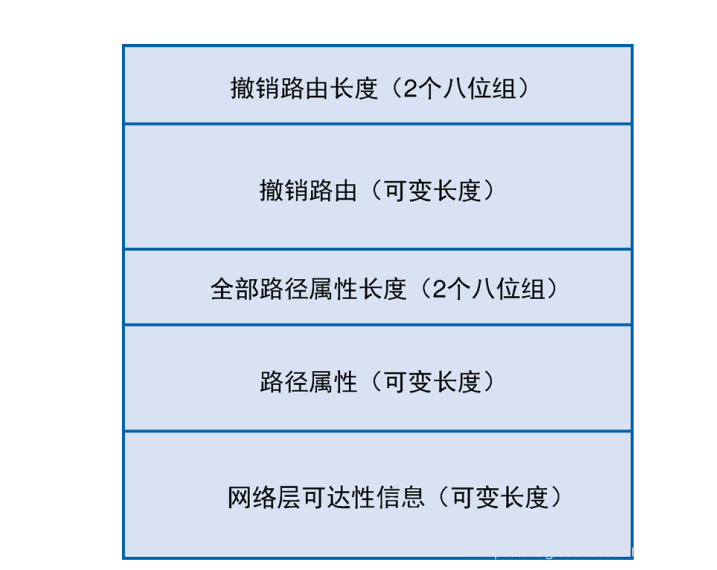
Update消息的格式如下图所示,其作用是向对等体宣告一条可行的路由或者撤销多条不可行的路由或者两者。
BGPUpdate消息包含以下字段。
- 不可行路由的长度(Unfeasible Routes Length):该字段长2个八位组,用于指示后面被撤销路由(Withdraw Routes)字段的长度(以八位组为单位),该字段值为0时表示没有被撤销的路由,且Update消息中无被撤销路由字段。
- 被撤销路由的长度(Withdrawn Routes Length):该字段长2个八位组,用于指示后面被撤销路由字段的总长度(以八位组为单位),该字段值为0时表示没有要撤销的路由,并且Update消息中无被撤销路由字段。
- 被撤销路由(WithdrawRoutes):该可变长度字段包含了一个要退出服务的路由列表,列表中的每条路由都以(长度,前缀)二元组形式加以表示,其中,长度表示前缀的长度,前缀表示被撤销路由的IP地址前缀。如果二元组中的长度部分为0,那么前缀部分将匹配所有路由。
- 整个路径属性的长度(Total Path AttributeLength):该字段长2个八位组,用于指示后面的路径属性字段的长度(以八位组为单位)。字段值为0时表示Update消息中未包含路径属性和NLRI。
- 路径属性(Path Attributes):该可变长度字段列出了与后面NLRI字段相关联的属性信息,每个路径属性者都以可变长度的三元组(属性类型,属性长度,属性值)进行表示,该三元组中的属性类型部分是一个长为2个八位组的字段,由4个标记比特、4个未用比特以及1个属性类型代码组成(见图2-21)。表2-4列出了最常见的一些属性类型代码以及母种属性类型的可能属性值。
- 网络层可达性信息(NetworkLayerReachabilityInformation):该可变长度字段包含一个(长度,前缀)二元组,其中,长度部分以比特为单位表示后面的前缀长度,前缀部分则是NLRI的IP地址前缀。如果长度部分取值为0,那么就表示前缀将匹配所有IP地址。
常见的路径属性包含以下几种:
| 属性 | 类别 | RFC | 应用 |
|---|
| ORIGIN | 公认必遵属性 | 4271 | 策路 |
| AS_PATH | 公认必遵属性 | 4271 | 策略、环路检测 |
| NEXT_HOP | 公认必遵属性 | 4271 | 策略 |
| LOCAL_PREF | 公认自决属性 | 4271 | 策略 |
| ATOMIC_AGGREGATE | 公认自决属性 | 4271 | 地址聚合 |
| COMMUNITY | 可选传递属性 | 1997 | 扩展 |
| AGGREGATOR | 可选传递属性 | 4271 | 地址聚合 |
| EXTENDED COMMUNITY | 可选传递属性 | 4360 | 扩展 |
| AS4_PATH | 可选传递属性 | 6793 | 扩展、策略 |
| AS4_AGGREGATOR | 可选传递属性 | 6793 | 扩展、地址聚合 |
| MULTI_EXIT_DISC(MED) | 可选非传递属性 | 4271 | 策路 |
| ORIGINATOR_ID | 可选非传递属性 | 4456 | 扩展、环路检测、策略 |
| CLUSTER_LIST | 可选非传递属性 | 4456 | 扩展、环路检测、策略 |
| Multiprotocol Reachable NLRI | 可选非传选属性 | 4760 | 多协议BGP |
| Multiprotocol Unreachable NLRI | 可选非传选属性 | 4760 | 多协议BGP |
Update消息处理
根据前面FSM的分析我们知道IO线程FD可读以后,会执行bgp_process_reads处理可读的事件,bgp_read 读取FD的报文消息,TCP是stream如何保证读取的是完整的报文,没有可能读取一半??
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| /*
* Reads a chunk of data from peer->fd into peer->ibuf_work.
*
* code_p
* Pointer to location to store FSM event code in case of fatal error.
*
* @return status flag (see top-of-file)
*
* PLEASE NOTE: If we ever transform the bgp_read to be a pthread
* per peer then we need to rethink the global ibuf_scratch
* data structure above.
*/
static uint16_t bgp_read(struct peer *peer, int *code_p)
{
size_t readsize; /* how many bytes we want to read */
ssize_t nbytes; /* how many bytes we actually read */
size_t ibuf_work_space; /* space we can read into the work buf */
uint16_t status = 0;
ibuf_work_space = ringbuf_space(peer->ibuf_work); //计算可用于读取的空间大小
if (ibuf_work_space == 0) { //空间不足处理
SET_FLAG(status, BGP_IO_WORK_FULL_ERR);
return status;
}
readsize = MIN(ibuf_work_space, sizeof(ibuf_scratch)); //要读取的字节数
nbytes = read(peer->fd, ibuf_scratch, readsize);
/* EAGAIN or EWOULDBLOCK; come back later */
if (nbytes < 0 && ERRNO_IO_RETRY(errno)) {
SET_FLAG(status, BGP_IO_TRANS_ERR);
} else if (nbytes < 0) {
/* Fatal error; tear down session */
flog_err(EC_BGP_UPDATE_RCV,
"%s [Error] bgp_read_packet error: %s", peer->host,
safe_strerror(errno));
/* Handle the error in the main pthread. */
if (code_p)
*code_p = TCP_fatal_error;
SET_FLAG(status, BGP_IO_FATAL_ERR);
} else if (nbytes == 0) {
/* Received EOF / TCP session closed */
if (bgp_debug_neighbor_events(peer))
zlog_debug("%s [Event] BGP connection closed fd %d",
peer->host, peer->fd);
/* Handle the error in the main pthread. */
if (code_p)
*code_p = TCP_connection_closed;
SET_FLAG(status, BGP_IO_FATAL_ERR);
} else {
assert(ringbuf_put(peer->ibuf_work, ibuf_scratch, nbytes) ==
(size_t)nbytes);
}
return status;
}
|
然后添加事件到主线程继续处理,主线程调用bgp_process_packet处理接收到的报文,其中处理update的消息的函数是bgp_update_receive。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| case BGP_MSG_UPDATE:
frrtrace(2, frr_bgp, update_process, peer, size);
atomic_fetch_add_explicit(&peer->update_in, 1,
memory_order_relaxed);
peer->readtime = monotime(NULL);
mprc = bgp_update_receive(peer, size);
if (mprc == BGP_Stop)
flog_err(
EC_BGP_UPDATE_RCV,
"%s: BGP UPDATE receipt failed for peer: %s",
__func__, peer->host);
break;
|
这个函数很大,我们分阶段来分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| /**
* Process BGP UPDATE message for peer.
*
* Parses UPDATE and creates attribute object.
*
* @param peer
* @param size size of the packet
* @return as in summary
*/
static int bgp_update_receive(struct peer *peer, bgp_size_t size)
{
int ret, nlri_ret;
uint8_t *end;
struct stream *s;
struct attr attr;
bgp_size_t attribute_len;
bgp_size_t update_len;
bgp_size_t withdraw_len;
bool restart = false;
enum NLRI_TYPES {
NLRI_UPDATE,
NLRI_WITHDRAW,
NLRI_MP_UPDATE,
NLRI_MP_WITHDRAW,
NLRI_TYPE_MAX
};
struct bgp_nlri nlris[NLRI_TYPE_MAX];
|
BGP 把 NLRI 分为4种,nlri是(network layer reachable infomation,网络层可达性信息)的缩写:
- NLRI_UPDATE
- NLRI_WITHDRAW
- NLRI_MP_UPDATE
- NLRI_MP_WITHDRAW
MP是Multiprotocol BGP 多协议BGP的简写,上面的代码引申出BGP新的两个数据结构:
struct bgp_nlri用于解析过程中的临时存储,解析完成后,用于后续的函数继续处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| /* This structure's member directly points incoming packet data
stream. */
struct bgp_nlri {
/* AFI. */
uint16_t afi; /* iana_afi_t */
/* SAFI. */
uint8_t safi; /* iana_safi_t */
/* Pointer to NLRI byte stream. */
uint8_t *nlri;
/* Length of whole NLRI. */
bgp_size_t length;
};
|
struct attr 是BGP 所有属性attribute的统一的结构体,包含了前面描述的BGP的所有属性信息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| /* BGP core attribute structure. */
struct attr {
/* AS Path structure */
struct aspath *aspath;
/* Community structure */
struct community *community;
/* Reference count of this attribute. */
unsigned long refcnt;
/* Flag of attribute is set or not. */
uint64_t flag;
/* Apart from in6_addr, the remaining static attributes */
struct in_addr nexthop;
uint32_t med;
uint32_t local_pref;
ifindex_t nh_ifindex;
/* Path origin attribute */
uint8_t origin;
/* PMSI tunnel type (RFC 6514). */
enum pta_type pmsi_tnl_type;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| /* Unfeasible Route Length. */
withdraw_len = stream_getw(s);
/* Unfeasible Route Length check. */
if (stream_pnt(s) + withdraw_len > end) {
flog_err(EC_BGP_UPDATE_RCV,
"%s [Error] Update packet error (packet unfeasible length overflow %d)",
peer->host, withdraw_len);
bgp_notify_send(peer, BGP_NOTIFY_UPDATE_ERR,
BGP_NOTIFY_UPDATE_MAL_ATTR);
return BGP_Stop;
}
/* Unfeasible Route packet format check. */
if (withdraw_len > 0) {
nlris[NLRI_WITHDRAW].afi = AFI_IP;
nlris[NLRI_WITHDRAW].safi = SAFI_UNICAST;
nlris[NLRI_WITHDRAW].nlri = stream_pnt(s);
nlris[NLRI_WITHDRAW].length = withdraw_len;
stream_forward_getp(s, withdraw_len);
}
|
首先解析报文里面是否携带了撤销路由,如果有则保存到nlris[NLRI_WITHDRAW]里面,并增加解析报文的长度withdraw_len,然后继续解析路径属性
解析路径属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| /* Certain attribute parsing errors should not be considered bad enough
* to reset the session for, most particularly any partial/optional
* attributes that have 'tunneled' over speakers that don't understand
* them. Instead we withdraw only the prefix concerned.
*
* Complicates the flow a little though..
*/
enum bgp_attr_parse_ret attr_parse_ret = BGP_ATTR_PARSE_PROCEED;
/* This define morphs the update case into a withdraw when lower levels
* have signalled an error condition where this is best.
*/
#define NLRI_ATTR_ARG (attr_parse_ret != BGP_ATTR_PARSE_WITHDRAW ? &attr : NULL)
/* Parse attribute when it exists. */
if (attribute_len) {
attr_parse_ret = bgp_attr_parse(peer, &attr, attribute_len,
&nlris[NLRI_MP_UPDATE],
&nlris[NLRI_MP_WITHDRAW]);
if (attr_parse_ret == BGP_ATTR_PARSE_ERROR) {
bgp_attr_unintern_sub(&attr);
return BGP_Stop;
}
}
|
bgp_attr_parse 接收来自对等体的BGP UPDATE消息,并解析该消息以创建相应的属性对象,因为报文中Path Attributes有很多,所以while循环里面处理所有的属性信息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| /* Read attribute of update packet. This function is called from
bgp_update_receive() in bgp_packet.c. */
enum bgp_attr_parse_ret bgp_attr_parse(struct peer *peer, struct attr *attr,
bgp_size_t size,
struct bgp_nlri *mp_update,
struct bgp_nlri *mp_withdraw)
{
enum bgp_attr_parse_ret ret;
uint8_t flag = 0;
uint8_t type = 0;
bgp_size_t length;
uint8_t *startp, *endp;
uint8_t *attr_endp;
uint8_t seen[BGP_ATTR_BITMAP_SIZE];
/* we need the as4_path only until we have synthesized the as_path with
* it */
/* same goes for as4_aggregator */
struct aspath *as4_path = NULL;
as_t as4_aggregator = 0;
struct in_addr as4_aggregator_addr = {.s_addr = 0};
struct transit *transit;
/* Initialize bitmap. */
memset(seen, 0, BGP_ATTR_BITMAP_SIZE);
/* End pointer of BGP attribute. */
endp = BGP_INPUT_PNT(peer) + size;
/* Get attributes to the end of attribute length. */
while (BGP_INPUT_PNT(peer) < endp) {
/* Check remaining length check.*/
if (endp - BGP_INPUT_PNT(peer) < BGP_ATTR_MIN_LEN) {
|
先获取flag和type,然后根据flag里面是否有BGP_ATTR_FLAG_EXTLEN用于MP的扩展字段,如果有那么长度是2个字节,否则是一个字节
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| /* Fetch attribute flag and type. */
startp = BGP_INPUT_PNT(peer);
/* "The lower-order four bits of the Attribute Flags octet are
unused. They MUST be zero when sent and MUST be ignored when
received." */
flag = 0xF0 & stream_getc(BGP_INPUT(peer));
type = stream_getc(BGP_INPUT(peer));
/* Check whether Extended-Length applies and is in bounds */
if (CHECK_FLAG(flag, BGP_ATTR_FLAG_EXTLEN)
&& ((endp - startp) < (BGP_ATTR_MIN_LEN + 1))) {
flog_warn(
EC_BGP_EXT_ATTRIBUTE_TOO_SMALL,
"%s: Extended length set, but just %lu bytes of attr header",
peer->host,
(unsigned long)(endp
- stream_pnt(BGP_INPUT(peer))));
bgp_notify_send(peer, BGP_NOTIFY_UPDATE_ERR,
BGP_NOTIFY_UPDATE_ATTR_LENG_ERR);
ret = BGP_ATTR_PARSE_ERROR;
goto done;
}
/* Check extended attribue length bit. */
if (CHECK_FLAG(flag, BGP_ATTR_FLAG_EXTLEN)) //与0x10比较
length = stream_getw(BGP_INPUT(peer)); //2个字节
else
length = stream_getc(BGP_INPUT(peer)); //1个字节
|
然后填充下面的结构体,以便后面继续处理,参数太多,写成一个结构体往下传递
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| /* Below exported for unit-test purposes only */
struct bgp_attr_parser_args {
struct peer *peer;
bgp_size_t length; /* attribute data length; */
bgp_size_t total; /* total length, inc header */
struct attr *attr;
uint8_t type;
uint8_t flags;
uint8_t *startp;
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| struct bgp_attr_parser_args attr_args = {
.peer = peer,
.length = length,
.attr = attr,
.type = type,
.flags = flag,
.startp = startp,
.total = attr_endp - startp,
};
|
然后根据属性的TYPE值,处理不同的属性,我们拿简单的BGP_ATTR_ORIGIN看下,其解析报文里面的origin值(1个字节),并赋值到attr里面,置位Flag |= BGP_ATTR_ORIGIN,attr是函数bgp_update_receive传下来的一个临时变量。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
| /* OK check attribute and store it's value. */
switch (type) {
case BGP_ATTR_ORIGIN:
ret = bgp_attr_origin(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_AS_PATH:
ret = bgp_attr_aspath(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_AS4_PATH:
ret = bgp_attr_as4_path(&attr_args, &as4_path);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_NEXT_HOP:
ret = bgp_attr_nexthop(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_MULTI_EXIT_DISC:
ret = bgp_attr_med(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_LOCAL_PREF:
ret = bgp_attr_local_pref(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_ATOMIC_AGGREGATE:
ret = bgp_attr_atomic(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_AGGREGATOR:
ret = bgp_attr_aggregator(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_AS4_AGGREGATOR:
ret = bgp_attr_as4_aggregator(&attr_args,
&as4_aggregator,
&as4_aggregator_addr);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_COMMUNITIES:
ret = bgp_attr_community(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_LARGE_COMMUNITIES:
ret = bgp_attr_large_community(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_ORIGINATOR_ID:
ret = bgp_attr_originator_id(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_CLUSTER_LIST:
ret = bgp_attr_cluster_list(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_MP_REACH_NLRI:
ret = bgp_mp_reach_parse(&attr_args, mp_update);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_MP_UNREACH_NLRI:
ret = bgp_mp_unreach_parse(&attr_args, mp_withdraw);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_EXT_COMMUNITIES:
ret = bgp_attr_ext_communities(&attr_args);
break;
#ifdef ENABLE_BGP_VNC_ATTR
case BGP_ATTR_VNC:
#endif
case BGP_ATTR_ENCAP:
ret = bgp_attr_encap(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_PREFIX_SID:
ret = bgp_attr_prefix_sid(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_PMSI_TUNNEL:
ret = bgp_attr_pmsi_tunnel(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_IPV6_EXT_COMMUNITIES:
ret = bgp_attr_ipv6_ext_communities(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_OTC:
ret = bgp_attr_otc(&attr_args);
break;
case BGP_ATTR_AIGP:
ret = bgp_attr_aigp(&attr_args);
break;
default:
ret = bgp_attr_unknown(&attr_args);
break;
}
|
Origin的解析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| /* Get origin attribute of the update message. */
static enum bgp_attr_parse_ret
bgp_attr_origin(struct bgp_attr_parser_args *args)
{
struct peer *const peer = args->peer;
struct attr *const attr = args->attr;
const bgp_size_t length = args->length;
/* If any recognized attribute has Attribute Length that conflicts
with the expected length (based on the attribute type code), then
the Error Subcode is set to Attribute Length Error. The Data
field contains the erroneous attribute (type, length and
value). */
if (length != 1) {
flog_err(EC_BGP_ATTR_LEN,
"Origin attribute length is not one %d", length);
return bgp_attr_malformed(args, BGP_NOTIFY_UPDATE_ATTR_LENG_ERR,
args->total);
}
/* Fetch origin attribute. */
attr->origin = stream_getc(BGP_INPUT(peer));
/* If the ORIGIN attribute has an undefined value, then the Error
Subcode is set to Invalid Origin Attribute. The Data field
contains the unrecognized attribute (type, length and value). */
if ((attr->origin != BGP_ORIGIN_IGP) && (attr->origin != BGP_ORIGIN_EGP)
&& (attr->origin != BGP_ORIGIN_INCOMPLETE)) {
flog_err(EC_BGP_ATTR_ORIGIN,
"Origin attribute value is invalid %d", attr->origin);
return bgp_attr_malformed(args, BGP_NOTIFY_UPDATE_INVAL_ORIGIN,
args->total);
}
/* Set oring attribute flag. */
attr->flag |= ATTR_FLAG_BIT(BGP_ATTR_ORIGIN);
return 0;
}
|
AS_PATH解析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| /* Parse AS path information. This function is wrapper of
aspath_parse. */
static int bgp_attr_aspath(struct bgp_attr_parser_args *args)
{
struct attr *const attr = args->attr;
struct peer *const peer = args->peer;
const bgp_size_t length = args->length;
enum asnotation_mode asnotation;
asnotation = bgp_get_asnotation(
args->peer && args->peer->bgp ? args->peer->bgp : NULL);
/*
* peer with AS4 => will get 4Byte ASnums
* otherwise, will get 16 Bit
*/
attr->aspath =
aspath_parse(peer->curr, length,
CHECK_FLAG(peer->cap, PEER_CAP_AS4_RCV) &&
CHECK_FLAG(peer->cap, PEER_CAP_AS4_ADV),
asnotation);
/* In case of IBGP, length will be zero. */
if (!attr->aspath) {
flog_err(EC_BGP_ATTR_MAL_AS_PATH,
"Malformed AS path from %s, length is %d", peer->host,
length);
return bgp_attr_malformed(args, BGP_NOTIFY_UPDATE_MAL_AS_PATH,
0);
}
/* Conformant BGP speakers SHOULD NOT send BGP
* UPDATE messages containing AS_SET or AS_CONFED_SET. Upon receipt of
* such messages, conformant BGP speakers SHOULD use the "Treat-as-
* withdraw" error handling behavior as per [RFC7606].
*/
if (peer->bgp && peer->bgp->reject_as_sets &&
aspath_check_as_sets(attr->aspath)) {
flog_err(EC_BGP_ATTR_MAL_AS_PATH,
"AS_SET and AS_CONFED_SET are deprecated from %pBP",
peer);
return bgp_attr_malformed(args, BGP_NOTIFY_UPDATE_MAL_AS_PATH,
0);
}
/* Set aspath attribute flag. */
attr->flag |= ATTR_FLAG_BIT(BGP_ATTR_AS_PATH); //按位或
return BGP_ATTR_PARSE_PROCEED;
}
|
存放的数据结构struct aspath
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| /* AS_PATH segment data in abstracted form, no limit is placed on length */
struct assegment {
struct assegment *next;
as_t *as;
unsigned short length;
uint8_t type;
};
/* AS path may be include some AsSegments. */
struct aspath {
/* Reference count to this aspath. */
unsigned long refcnt;
/* segment data */
struct assegment *segments;
/* AS path as a json object */
json_object *json;
/* String expression of AS path. This string is used by vty output
and AS path regular expression match. */
char *str;
unsigned short str_len;
/* AS notation used by string expression of AS path */
enum asnotation_mode asnotation;
};
|
真正的AS号存放在struct assegment的as里面,type/length对应的是AS_PATH报文的内容,str是翻译为人可以读的内容比如100,400
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| /* AS path parse function. pnt is a pointer to byte stream and length
is length of byte stream. If there is same AS path in the the AS
path hash then return it else make new AS path structure.
On error NULL is returned.
*/
struct aspath *aspath_parse(struct stream *s, size_t length, int use32bit,
enum asnotation_mode asnotation)
{
struct aspath as;
struct aspath *find;
/* If length is odd it's malformed AS path. */
/* Nit-picking: if (use32bit == 0) it is malformed if odd,
* otherwise its malformed when length is larger than 2 and (length-2)
* is not dividable by 4.
* But... this time we're lazy
*/
if (length % AS16_VALUE_SIZE)
return NULL;
memset(&as, 0, sizeof(as));
as.asnotation = asnotation;
if (assegments_parse(s, length, &as.segments, use32bit) < 0) //assegments_parse根据报文解析并创建segments
return NULL;
/* If already same aspath exist then return it. */
find = hash_get(ashash, &as, aspath_hash_alloc); //aspath_hash_alloc创建新的aspath
/* if the aspath was already hashed free temporary memory. */
if (find->refcnt) {
assegment_free_all(as.segments);
/* aspath_key_make() always updates the string */
XFREE(MTYPE_AS_STR, as.str);
if (as.json) {
json_object_free(as.json);
as.json = NULL;
}
}
find->refcnt++;
return find;
}
|
assegments_parse根据报文解析并创建segments,然后aspath_hash_alloc创建新的aspath并hash加入全局的ashash的全局HASH表里面。
其余的路径解析这里不再分析,等后面业务遇到的时候在继续分析。
当所有的路径属性解析完成后,需要做一次检查,检查所有的公认必遵的属性是否全部包含,否则是有问题的,返回错误
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| /* Check all mandatory well-known attributes are present */
ret = bgp_attr_check(peer, attr);
if (ret < 0)
goto done;
/*
* At this place we can see whether we got AS4_PATH and/or
* AS4_AGGREGATOR from a 16Bit peer and act accordingly.
* We can not do this before we've read all attributes because
* the as4 handling does not say whether AS4_PATH has to be sent
* after AS_PATH or not - and when AS4_AGGREGATOR will be send
* in relationship to AGGREGATOR.
* So, to be defensive, we are not relying on any order and read
* all attributes first, including these 32bit ones, and now,
* afterwards, we look what and if something is to be done for as4.
*
* It is possible to not have AS_PATH, e.g. GR EoR and sole
* MP_UNREACH_NLRI.
*/
/* actually... this doesn't ever return failure currently, but
* better safe than sorry */
if (CHECK_FLAG(attr->flag, ATTR_FLAG_BIT(BGP_ATTR_AS_PATH))
&& bgp_attr_munge_as4_attrs(peer, attr, as4_path, as4_aggregator,
&as4_aggregator_addr)) {
bgp_notify_send(peer, BGP_NOTIFY_UPDATE_ERR,
BGP_NOTIFY_UPDATE_MAL_ATTR);
ret = BGP_ATTR_PARSE_ERROR;
goto done;
}
|
至此UPDATE报文里面的属性全部解析完成,存放在 attr 的局部变量里面。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| /* Parse attribute when it exists. */
if (attribute_len) {
attr_parse_ret = bgp_attr_parse(peer, &attr, attribute_len,
&nlris[NLRI_MP_UPDATE],
&nlris[NLRI_MP_WITHDRAW]);
if (attr_parse_ret == BGP_ATTR_PARSE_ERROR) {
bgp_attr_unintern_sub(&attr);
return BGP_Stop;
}
}
|
处理NLRI
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| /* Network Layer Reachability Information. */
update_len = end - stream_pnt(s);
if (update_len && attribute_len) {
/* Set NLRI portion to structure. */
nlris[NLRI_UPDATE].afi = AFI_IP;
nlris[NLRI_UPDATE].safi = SAFI_UNICAST;
nlris[NLRI_UPDATE].nlri = stream_pnt(s);
nlris[NLRI_UPDATE].length = update_len;
stream_forward_getp(s, update_len);
if (CHECK_FLAG(attr.flag, ATTR_FLAG_BIT(BGP_ATTR_MP_REACH_NLRI))) {
/*
* We skipped nexthop attribute validation earlier so
* validate the nexthop now.
*/
if (bgp_attr_nexthop_valid(peer, &attr) < 0) {
bgp_attr_unintern_sub(&attr);
return BGP_Stop;
}
}
}
|
获取NLRI的报文长度,填入nlris[NLRI_UPDATE],到现在为止nlris里面的4种类型(如果有的话),已经全部填写到nlris数组结构体里面
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| /* Parse any given NLRIs */
for (int i = NLRI_UPDATE; i < NLRI_TYPE_MAX; i++) {
if (!nlris[i].nlri)
continue;
/* NLRI is processed iff the peer if configured for the specific
* afi/safi */
if (!peer->afc[nlris[i].afi][nlris[i].safi]) {
zlog_info(
"%s [Info] UPDATE for non-enabled AFI/SAFI %u/%u",
peer->host, nlris[i].afi, nlris[i].safi);
continue;
}
/* EoR handled later */
if (nlris[i].length == 0)
continue;
switch (i) {
case NLRI_UPDATE:
case NLRI_MP_UPDATE:
nlri_ret = bgp_nlri_parse(peer, NLRI_ATTR_ARG,
&nlris[i], 0);
break;
case NLRI_WITHDRAW:
case NLRI_MP_WITHDRAW:
nlri_ret = bgp_nlri_parse(peer, NLRI_ATTR_ARG,
&nlris[i], 1);
break;
default:
nlri_ret = BGP_NLRI_PARSE_ERROR;
}
|
然后我们遍历这个数组,处理里面所有的NLRI的类型,本次先分析 NLRI_UPDATE ,MP后面再分析。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| /**
* Frontend for NLRI parsing, to fan-out to AFI/SAFI specific parsers.
*
* mp_withdraw, if set, is used to nullify attr structure on most of the
* calling safi function and for evpn, passed as parameter
*/
int bgp_nlri_parse(struct peer *peer, struct attr *attr,
struct bgp_nlri *packet, bool mp_withdraw)
{
switch (packet->safi) {
case SAFI_UNICAST:
case SAFI_MULTICAST:
return bgp_nlri_parse_ip(peer, mp_withdraw ? NULL : attr,
packet);
case SAFI_LABELED_UNICAST:
return bgp_nlri_parse_label(peer, mp_withdraw ? NULL : attr,
packet);
case SAFI_MPLS_VPN:
return bgp_nlri_parse_vpn(peer, mp_withdraw ? NULL : attr,
packet);
case SAFI_EVPN:
return bgp_nlri_parse_evpn(peer, attr, packet, mp_withdraw);
case SAFI_FLOWSPEC:
return bgp_nlri_parse_flowspec(peer, attr, packet, mp_withdraw);
}
return BGP_NLRI_PARSE_ERROR;
}
|
根据前面解析出来的SAFI选取不同的处理函数,afi/safi定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| /* Address family numbers from RFC1700. */
typedef enum {
AFI_UNSPEC = 0, //未指定的AFI类型
AFI_IP = 1, //IPv4地址家族
AFI_IP6 = 2, // IPv6地址家族,表示IPv6路由信息。
AFI_L2VPN = 3, //Layer 2 VPN地址家族,用于表示层2虚拟专用网络的路由信息。
AFI_MAX = 4 //AFI类型的最大值。
} afi_t;
#define IS_VALID_AFI(a) ((a) > AFI_UNSPEC && (a) < AFI_MAX)
/* Subsequent Address Family Identifier. */
typedef enum {
SAFI_UNSPEC = 0, //未指定的SAFI类型
SAFI_UNICAST = 1, //单播路由
SAFI_MULTICAST = 2, //多播路由,
SAFI_MPLS_VPN = 3, // MPLS VPN路由
SAFI_ENCAP = 4, // Encapsulation SAFI,表示封装(Encapsulation)路由信息
SAFI_EVPN = 5, //Ethernet VPN(EVPN),用于在数据中心网络中传输以太网以及与以太网相关的服务的VPN路由信息
SAFI_LABELED_UNICAST = 6, //带标签的单播路由
SAFI_FLOWSPEC = 7, //流规格(Flowspec)路由,表示用于描述流量特性和策略的路由信息
SAFI_MAX = 8 //SAFI类型的最大值
} safi_t;
|
可以从下面的函数查看组合:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| static inline int afindex(afi_t afi, safi_t safi)
{
switch (afi) {
case AFI_IP:
switch (safi) {
case SAFI_UNICAST:
return BGP_AF_IPV4_UNICAST;
case SAFI_MULTICAST:
return BGP_AF_IPV4_MULTICAST;
case SAFI_LABELED_UNICAST:
return BGP_AF_IPV4_LBL_UNICAST;
case SAFI_MPLS_VPN:
return BGP_AF_IPV4_VPN;
case SAFI_ENCAP:
return BGP_AF_IPV4_ENCAP;
case SAFI_FLOWSPEC:
return BGP_AF_IPV4_FLOWSPEC;
case SAFI_EVPN:
case SAFI_UNSPEC:
case SAFI_MAX:
return BGP_AF_MAX;
}
break;
case AFI_IP6:
switch (safi) {
case SAFI_UNICAST:
return BGP_AF_IPV6_UNICAST;
case SAFI_MULTICAST:
return BGP_AF_IPV6_MULTICAST;
case SAFI_LABELED_UNICAST:
return BGP_AF_IPV6_LBL_UNICAST;
case SAFI_MPLS_VPN:
return BGP_AF_IPV6_VPN;
case SAFI_ENCAP:
return BGP_AF_IPV6_ENCAP;
case SAFI_FLOWSPEC:
return BGP_AF_IPV6_FLOWSPEC;
case SAFI_EVPN:
case SAFI_UNSPEC:
case SAFI_MAX:
return BGP_AF_MAX;
}
break;
case AFI_L2VPN:
switch (safi) {
case SAFI_EVPN:
return BGP_AF_L2VPN_EVPN;
case SAFI_UNICAST:
case SAFI_MULTICAST:
case SAFI_LABELED_UNICAST:
case SAFI_MPLS_VPN:
case SAFI_ENCAP:
case SAFI_FLOWSPEC:
case SAFI_UNSPEC:
case SAFI_MAX:
return BGP_AF_MAX;
}
break;
case AFI_UNSPEC:
case AFI_MAX:
return BGP_AF_MAX;
}
assert(!"Reached end of function we should never hit");
}
|
IP + UNICAST/ MULTICAST 将调用bgp_nlri_parse_ip函数,NLRI里面存放的是前缀:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| /* Parse NLRI stream. Withdraw NLRI is recognized by NULL attr
value. */
int bgp_nlri_parse_ip(struct peer *peer, struct attr *attr,
struct bgp_nlri *packet)
{
uint8_t *pnt;
uint8_t *lim;
struct prefix p;
int psize;
afi_t afi;
safi_t safi;
bool addpath_capable;
uint32_t addpath_id;
pnt = packet->nlri;
lim = pnt + packet->length;
afi = packet->afi;
safi = packet->safi;
addpath_id = 0;
addpath_capable = bgp_addpath_encode_rx(peer, afi, safi);
|
这里又引出BGP的一个数据结构struct prefix
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| /* FRR generic prefix structure. */
struct prefix {
uint8_t family; //表示前缀的地址家族,指明了前缀的类型,可以是IPv4、IPv6、以太网等
uint16_t prefixlen; //表示前缀的长度,即网络前缀的位数。
union {
uint8_t prefix; // 一个字节的前缀信息,用于存储某些特定类型的前缀
struct in_addr prefix4; // IPv4地址类型的前缀信息
struct in6_addr prefix6; //IPv6地址类型的前缀信息。
struct {
struct in_addr id;
struct in_addr adv_router;
} lp;
struct ethaddr prefix_eth; /* AF_ETHERNET */
uint8_t val[16];
uint32_t val32[4];
uintptr_t ptr;
struct evpn_addr prefix_evpn; /* AF_EVPN */
struct flowspec_prefix prefix_flowspec; /* AF_FLOWSPEC */
} u __attribute__((aligned(8)));
};
|
在每次的for循环里面,需要填充好prefix前缀里面的长度、 family 、前缀值,然后以便后续bgp_update函数继续处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| /* Fetch prefix length. */
p.prefixlen = *pnt++;
/* afi/safi validity already verified by caller,
* bgp_update_receive */
p.family = afi2family(afi);
/* Packet size overflow check. */
psize = PSIZE(p.prefixlen);
/* Fetch prefix from NLRI packet. */
memcpy(p.u.val, pnt, psize);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| /* Normal process. */
if (attr)
bgp_update(peer, &p, addpath_id, attr, afi, safi,
ZEBRA_ROUTE_BGP, BGP_ROUTE_NORMAL, NULL,
NULL, 0, 0, NULL);
else
bgp_withdraw(peer, &p, addpath_id, afi, safi,
ZEBRA_ROUTE_BGP, BGP_ROUTE_NORMAL, NULL,
NULL, 0, NULL);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| void bgp_update(struct peer *peer, const struct prefix *p, uint32_t addpath_id,
struct attr *attr, afi_t afi, safi_t safi, int type,
int sub_type, struct prefix_rd *prd, mpls_label_t *label,
uint32_t num_labels, int soft_reconfig,
struct bgp_route_evpn *evpn)
{
int ret;
int aspath_loop_count = 0;
struct bgp_dest *dest;
|
bgp_update函数引申出struct bgp_dest数据结构,因为在bgp_table.h中定义了#define bgp_dest bgp_node,实际上就是struct bgp_node,是BGP 存放路由的关键数据结构,我们先认识下,使用关键字prefix组织成radix树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| /*
* Macro that defines all fields in a route node.
*/
#define ROUTE_NODE_FIELDS \
/* Actual prefix of this radix. */ \
struct prefix p; \
\
/* Tree link. */ \
struct route_table *table_rdonly(table); /* 指向路由表的指针,以只读方式访问 */ \
struct route_node *table_rdonly(parent); /* 指向父节点的指针,以只读方式访问 */ \
struct route_node *table_rdonly(link[2]); /* 包含两个指针的数组,表示左右两个子节点 */ \
\
/* Lock of this radix */ \
unsigned int table_rdonly(lock); /* 表示该节点的锁,以只读方式访问 */ \
\
struct rn_hash_node_item nodehash; /* 用于哈希的节点项 */ \
/* Each node of route. */ \
void *info; /* 每个节点的信息 */ \
/* Each routing entry. */
struct route_node { //该结构体能够表示路由表中的一个节点,包含了该节点的各种信息和链接关系
ROUTE_NODE_FIELDS //包含 ROUTE_NODE_FIELDS 宏展开后的所有字段
#define l_left link[0]
#define l_right link[1]
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| struct bgp_node {
/*
* CAUTION
*
* These fields must be the very first fields in this structure.
*
* @see bgp_node_to_rnode
* @see bgp_node_from_rnode
*/
ROUTE_NODE_FIELDS
struct bgp_adj_out_rb adj_out;
struct bgp_adj_in *adj_in;
struct bgp_dest *pdest;
STAILQ_ENTRY(bgp_dest) pq;
uint64_t version;
mpls_label_t local_label;
uint16_t flags;
#define BGP_NODE_PROCESS_SCHEDULED (1 << 0)
#define BGP_NODE_USER_CLEAR (1 << 1)
#define BGP_NODE_LABEL_CHANGED (1 << 2)
#define BGP_NODE_REGISTERED_FOR_LABEL (1 << 3)
#define BGP_NODE_SELECT_DEFER (1 << 4)
#define BGP_NODE_FIB_INSTALL_PENDING (1 << 5)
#define BGP_NODE_FIB_INSTALLED (1 << 6)
#define BGP_NODE_LABEL_REQUESTED (1 << 7)
#define BGP_NODE_SOFT_RECONFIG (1 << 8)
struct bgp_addpath_node_data tx_addpath;
enum bgp_path_selection_reason reason;
};
|
bgp_update引入了bgp_path_info数据结构,该结构体包含了一条BGP路径的各种信息,用于描述从源到目的的路由路径
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| void bgp_update(struct peer *peer, const struct prefix *p, uint32_t addpath_id,
struct attr *attr, afi_t afi, safi_t safi, int type,
int sub_type, struct prefix_rd *prd, mpls_label_t *label,
uint32_t num_labels, int soft_reconfig,
struct bgp_route_evpn *evpn)
{
int ret;
int aspath_loop_count = 0;
struct bgp_dest *dest;
struct bgp *bgp;
struct attr new_attr;
struct attr *attr_new;
struct bgp_path_info *pi;
struct bgp_path_info *new = NULL;
struct bgp_path_info_extra *extra;
const char *reason;
char pfx_buf[BGP_PRD_PATH_STRLEN];
int connected = 0;
int do_loop_check = 1;
int has_valid_label = 0;
afi_t nh_afi;
bool force_evpn_import = false;
safi_t orig_safi = safi;
bool leak_success = true;
int allowas_in = 0;
if (frrtrace_enabled(frr_bgp, process_update)) {
char pfxprint[PREFIX2STR_BUFFER];
prefix2str(p, pfxprint, sizeof(pfxprint));
frrtrace(6, frr_bgp, process_update, peer, pfxprint, addpath_id,
afi, safi, attr);
}
#ifdef ENABLE_BGP_VNC
int vnc_implicit_withdraw = 0;
#endif
int same_attr = 0;
const struct prefix *bgp_nht_param_prefix;
/* Special case for BGP-LU - map LU safi to ordinary unicast safi */
if (orig_safi == SAFI_LABELED_UNICAST)
safi = SAFI_UNICAST;
memset(&new_attr, 0, sizeof(new_attr));
new_attr.label_index = BGP_INVALID_LABEL_INDEX;
new_attr.label = MPLS_INVALID_LABEL;
bgp = peer->bgp;
dest = bgp_afi_node_get(bgp->rib[afi][safi], afi, safi, p, prd);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| struct bgp_path_info {
/* For linked list. */
struct bgp_path_info *next; //指向下一条BGP路径信息的指针,用于构建路径信息的链表
struct bgp_path_info *prev; //指向上一条BGP路径信息的指针
/* For nexthop linked list */
LIST_ENTRY(bgp_path_info) nh_thread;
/* Back pointer to the prefix node */
struct bgp_dest *net;
/* Back pointer to the nexthop structure */
struct bgp_nexthop_cache *nexthop;
/* Peer structure. */
struct peer *peer;
/* Attribute structure. */
struct attr *attr;
/* Extra information */
struct bgp_path_info_extra *extra;
/* Multipath information */
struct bgp_path_info_mpath *mpath;
/* Uptime. */
time_t uptime;
/* reference count */
int lock;
|
bgp_afi_node_get在bgp对应的afi/safi table里面使用prefix前缀,获取struct bgp_node节点,并加入afi/safi table的二叉树里面。
如果需要记录adj_in,那么把当前的信息存入bgp_adj_in结构体,然后link到bgp_node的链表上面。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| /* When peer's soft reconfiguration enabled. Record input packet in
Adj-RIBs-In. */
if (!soft_reconfig &&
CHECK_FLAG(peer->af_flags[afi][safi], PEER_FLAG_SOFT_RECONFIG) &&
peer != bgp->peer_self) {
/*
* If the trigger is not from soft_reconfig and if
* PEER_FLAG_SOFT_RECONFIG is enabled for the peer, then attr
* will not be interned. In which case, it is ok to update the
* attr->evpn_overlay, so that, this can be stored in adj_in.
*/
if ((afi == AFI_L2VPN) && evpn) {
memcpy(&attr->evpn_overlay, evpn,
sizeof(struct bgp_route_evpn));
}
bgp_adj_in_set(dest, peer, attr, addpath_id);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| void bgp_adj_in_set(struct bgp_dest *dest, struct peer *peer, struct attr *attr,
uint32_t addpath_id)
{
struct bgp_adj_in *adj;
for (adj = dest->adj_in; adj; adj = adj->next) {
if (adj->peer == peer && adj->addpath_rx_id == addpath_id) {
if (adj->attr != attr) {
bgp_attr_unintern(&adj->attr);
adj->attr = bgp_attr_intern(attr);
}
return;
}
}
adj = XCALLOC(MTYPE_BGP_ADJ_IN, sizeof(struct bgp_adj_in));
adj->peer = peer_lock(peer); /* adj_in peer reference */
adj->attr = bgp_attr_intern(attr);
adj->uptime = monotime(NULL);
adj->addpath_rx_id = addpath_id;
BGP_ADJ_IN_ADD(dest, adj);
bgp_dest_lock_node(dest);
}
|
struc bgp_adj_in数据结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| /* BGP adjacency in. */
struct bgp_adj_in {
/* Linked list pointer. */
struct bgp_adj_in *next;
struct bgp_adj_in *prev;
/* Received peer. */
struct peer *peer;
/* Received attribute. */
struct attr *attr;
/* timestamp (monotime) */
time_t uptime;
/* Addpath identifier */
uint32_t addpath_rx_id;
};
|
然后会进行AS_PATH的防环检查,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| /* AS path loop check. */
if (do_loop_check) {
if (aspath_loop_check(attr->aspath, bgp->as) >
peer->allowas_in[afi][safi]) {
peer->stat_pfx_aspath_loop++;
reason = "as-path contains our own AS;";
goto filtered;
}
}
|
bgp_update中其他几个函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| attr_new = bgp_attr_intern(&new_attr); //会根据前面解析的attr(局部变量传下来的),申请一个attr_new,以便后续保存。
/* Make new BGP info. */
new = info_make(type, sub_type, 0, peer, attr_new, dest); //会创建一个新的struct bgp_path_info数据结构, attr_new 便保存在里面的,后续会在给bgp_path_info赋值。
/* If maximum prefix count is configured and current prefix
* count exeed it.
*/
if (bgp_maximum_prefix_overflow(peer, afi, safi, 0)) { //会检查BGP Max Prefix条目限制
reason = "maximum-prefix overflow";
bgp_attr_flush(&new_attr);
goto filtered;
}
/* Addpath ID */
new->addpath_rx_id = addpath_id;
/* Increment prefix */
bgp_aggregate_increment(bgp, p, new, afi, safi);
/* Register new BGP information. */
bgp_path_info_add(dest, new); //会把新的bgp_path_info,连接到bgp_node里面。
/* route_node_get lock */
bgp_dest_unlock_node(dest);
/* Process change. */
bgp_process(bgp, dest, afi, safi); //会把rn入队work_queue,后续work_queue注册的回调函数bgp_process_wq,会出队继续处理rn,而work_queue是在初始化的时候,就已经初始化好了
|
在bgp_route.h宏中定义了#define bgp_path_info_add(A, B) bgp_path_info_add_with_caller(__func__, (A), (B)):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| void bgp_path_info_add_with_caller(const char *name, struct bgp_dest *dest,
struct bgp_path_info *pi)
{
frrtrace(3, frr_bgp, bgp_path_info_add, dest, pi, name);
struct bgp_path_info *top;
top = bgp_dest_get_bgp_path_info(dest);
pi->next = top;
pi->prev = NULL;
if (top)
top->prev = pi;
bgp_dest_set_bgp_path_info(dest, pi);
bgp_path_info_lock(pi);
bgp_dest_lock_node(dest);
peer_lock(pi->peer); /* bgp_path_info peer reference */
bgp_dest_set_defer_flag(dest, false);
hook_call(bgp_snmp_update_stats, dest, pi, true);
}
|
接下来我们看看 WORK QUEUE(工作队列)
1
| bgp_process_queue_init(bgp);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| void bgp_process_queue_init(struct bgp *bgp)
{
if (!bgp->process_queue) {
char name[BUFSIZ];
snprintf(name, BUFSIZ, "process_queue %s", bgp->name_pretty);
bgp->process_queue = work_queue_new(bm->master, name);
}
bgp->process_queue->spec.workfunc = &bgp_process_wq;
bgp->process_queue->spec.del_item_data = &bgp_processq_del;
bgp->process_queue->spec.max_retries = 0;
bgp->process_queue->spec.hold = 50;
/* Use a higher yield value of 50ms for main queue processing */
bgp->process_queue->spec.yield = 50 * 1000L;
}
|
work queue的回调函数bgp_process_wq出队queue继续处理,bgp_process_main_one 处理具体的queue node,即bgp route_node的信息,这里提个问题,单线程处理的bgpd,为何这里需要在异步下work_queue继续处理??
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| static wq_item_status bgp_process_wq(struct work_queue *wq, void *data)
{
struct bgp_process_queue *pqnode = data;
struct bgp *bgp = pqnode->bgp;
struct bgp_table *table;
struct bgp_dest *dest;
/* eoiu marker */
if (CHECK_FLAG(pqnode->flags, BGP_PROCESS_QUEUE_EOIU_MARKER)) {
bgp_process_main_one(bgp, NULL, 0, 0);
/* should always have dedicated wq call */
assert(STAILQ_FIRST(&pqnode->pqueue) == NULL);
return WQ_SUCCESS;
}
while (!STAILQ_EMPTY(&pqnode->pqueue)) {
dest = STAILQ_FIRST(&pqnode->pqueue);
STAILQ_REMOVE_HEAD(&pqnode->pqueue, pq);
STAILQ_NEXT(dest, pq) = NULL; /* complete unlink */
table = bgp_dest_table(dest);
/* note, new DESTs may be added as part of processing */
bgp_process_main_one(bgp, dest, table->afi, table->safi);
bgp_dest_unlock_node(dest);
bgp_table_unlock(table);
}
return WQ_SUCCESS;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| /*
* old_select = The old best path
* new_select = the new best path
*
* if (!old_select && new_select)
* We are sending new information on.
*
* if (old_select && new_select) {
* if (new_select != old_select)
* We have a new best path send a change
* else
* We've received a update with new attributes that needs
* to be passed on.
* }
*
* if (old_select && !new_select)
* We have no eligible route that we can announce or the rn
* is being removed.
*/
static void bgp_process_main_one(struct bgp *bgp, struct bgp_dest *dest,
afi_t afi, safi_t safi)
{
struct bgp_path_info *new_select;
struct bgp_path_info *old_select;
struct bgp_path_info_pair old_and_new;
int debug = 0;
mpls_label_t mpls_label_null;
|
bgp_process_main_one 会根据BGP的选路原则选择一个最优的路由,选择原则如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| void bgp_best_selection(struct bgp *bgp, struct bgp_dest *dest,
struct bgp_maxpaths_cfg *mpath_cfg,
struct bgp_path_info_pair *result, afi_t afi,
safi_t safi)
{
struct bgp_path_info *new_select;
struct bgp_path_info *old_select;
|
然后group_announce_route发布路由,会遍历bgp->update_groups的HASH表,执行回调函数update_group_walkcb,最后会调到函数group_announce_route_walkcb
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| group_announce_route(bgp, afi, safi, dest, new_select);
/* unicast routes must also be annouced to
* labeled-unicast update-groups */
if (safi == SAFI_UNICAST)
group_announce_route(bgp, afi,
SAFI_LABELED_UNICAST, dest,
new_select);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| /*
* Go through all update subgroups and set up the adv queue for the
* input route.
*/
void group_announce_route(struct bgp *bgp, afi_t afi, safi_t safi,
struct bgp_dest *dest, struct bgp_path_info *pi)
{
struct updwalk_context ctx;
ctx.pi = pi;
ctx.dest = dest;
/* If suppress fib is enabled, the route will be advertised when
* FIB status is received
*/
if (!bgp_check_advertise(bgp, dest))
return;
update_group_af_walk(bgp, afi, safi, group_announce_route_walkcb, &ctx);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| void update_group_af_walk(struct bgp *bgp, afi_t afi, safi_t safi,
updgrp_walkcb cb, void *ctx)
{
struct updwalk_context wctx;
int afid;
if (!bgp)
return;
afid = afindex(afi, safi);
if (afid >= BGP_AF_MAX)
return;
memset(&wctx, 0, sizeof(wctx));
wctx.cb = cb;
wctx.context = ctx;
if (bgp->update_groups[afid])
hash_walk(bgp->update_groups[afid], update_group_walkcb, &wctx);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| static int update_group_walkcb(struct hash_bucket *bucket, void *arg)
{
struct update_group *updgrp = bucket->data;
struct updwalk_context *wctx = arg;
int ret = (*wctx->cb)(updgrp, wctx->context);
return ret;
}
|
而这里涉及到的结构体struct update_group/ struct update_subgroup是在bgp_establish的时候调用update_group_adjust_peer_afs创建的
1
2
| /* assign update-group/subgroup */
update_group_adjust_peer_afs(peer);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| /*
* update_group_adjust_peer_afs
*
* Adjust all peer_af structures for the given peer.
*/
static inline void update_group_adjust_peer_afs(struct peer *peer)
{
struct peer_af *paf;
int afidx;
for (afidx = BGP_AF_START; afidx < BGP_AF_MAX; afidx++) {
paf = peer->peer_af_array[afidx];
if (paf != NULL)
update_group_adjust_peer(paf);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| /*
* update_group_adjust_peer
*/
void update_group_adjust_peer(struct peer_af *paf)
{
struct update_group *updgrp;
struct update_subgroup *subgrp, *old_subgrp;
struct peer *peer;
if (!paf)
return;
peer = PAF_PEER(paf);
if (!peer_established(peer)) {
return;
}
if (!CHECK_FLAG(peer->flags, PEER_FLAG_CONFIG_NODE)) {
return;
}
if (!peer->afc_nego[paf->afi][paf->safi]) {
return;
}
updgrp = update_group_find(paf);
if (!updgrp)
updgrp = update_group_create(paf);
old_subgrp = paf->subgroup;
if (old_subgrp) {
/*
* If the update group of the peer is unchanged, the peer can
* stay
* in its existing subgroup and we're done.
*/
if (old_subgrp->update_group == updgrp)
return;
/*
* The peer is switching between update groups. Put it in its
* own subgroup under the new update group.
*/
update_subgroup_split_peer(paf, updgrp);
return;
}
subgrp = update_subgroup_find(updgrp, paf);
if (!subgrp)
subgrp = update_subgroup_create(updgrp);
update_subgroup_add_peer(subgrp, paf, 1);
if (BGP_DEBUG(update_groups, UPDATE_GROUPS))
zlog_debug("u%" PRIu64 ":s%" PRIu64 " add peer %s", updgrp->id,
subgrp->id, paf->peer->host);
return;
}
|
回到group_announce_route_walkcb函数,遍历group下的subgroup,然后得到struct bgp_path_info和bgp_node,调用函数subgroup_process_announce_selected,最后调用bgp_adj_out_set_subgroup 加入sync->update表,等待定时器更新发送,但此时传入定时器的时间为0,所以应该是一个实时的时间,此时相当于又异步了一次。
事件执行会调用bgp_generate_updgrp_packets,然后调用subgroup_update_packet,在该函数里面封装发送的UPDATE报文,其中bgp_packet_attribute封装属性,报文封装好后,调用bpacket_reformat_for_peer修正下报文的nexthop,然后调用bgp_packet_add把报文加入到peer的obuf里面,然后调用bgp_writes_on(peer),等fd可写的时候,IO线程会把UPDATE报文发送出去。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
| /*
* Generate advertisement information (withdraws, updates, EOR) from each
* update group a peer belongs to, encode this information into packets, and
* enqueue the packets onto the peer's output buffer.
*/
void bgp_generate_updgrp_packets(struct event *thread)
{
struct peer *peer = EVENT_ARG(thread);
struct stream *s;
struct peer_af *paf;
struct bpacket *next_pkt;
uint32_t wpq;
uint32_t generated = 0;
afi_t afi;
safi_t safi;
wpq = atomic_load_explicit(&peer->bgp->wpkt_quanta,
memory_order_relaxed);
/*
* The code beyond this part deals with update packets, proceed only
* if peer is Established and updates are not on hold (as part of
* update-delay processing).
*/
if (!peer_established(peer))
return;
if ((peer->bgp->main_peers_update_hold)
|| bgp_update_delay_active(peer->bgp))
return;
if (peer->t_routeadv)
return;
/*
* Since the following is a do while loop
* let's stop adding to the outq if we are
* already at the limit.
*/
if (peer->obuf->count >= bm->outq_limit) {
bgp_write_proceed_actions(peer);
return;
}
do {
enum bgp_af_index index;
s = NULL;
for (index = BGP_AF_START; index < BGP_AF_MAX; index++) {
paf = peer->peer_af_array[index];
if (!paf || !PAF_SUBGRP(paf))
continue;
afi = paf->afi;
safi = paf->safi;
next_pkt = paf->next_pkt_to_send;
/*
* Try to generate a packet for the peer if we are at
* the end of the list. Always try to push out
* WITHDRAWs first.
*/
if (!next_pkt || !next_pkt->buffer) {
next_pkt = subgroup_withdraw_packet(
PAF_SUBGRP(paf));
if (!next_pkt || !next_pkt->buffer)
subgroup_update_packet(PAF_SUBGRP(paf));
next_pkt = paf->next_pkt_to_send;
}
/*
* If we still don't have a packet to send to the peer,
* then try to find out out if we have to send eor or
* if not, skip to the next AFI, SAFI. Don't send the
* EOR prematurely; if the subgroup's coalesce timer is
* running, the adjacency-out structure is not created
* yet.
*/
if (!next_pkt || !next_pkt->buffer) {
if (!paf->t_announce_route) {
/* Make sure we supress BGP UPDATES
* for normal processing later again.
*/
UNSET_FLAG(paf->subgroup->sflags,
SUBGRP_STATUS_FORCE_UPDATES);
/* If route-refresh BoRR message was
* already sent and we are done with
* re-announcing tables for a decent
* afi/safi, we ready to send
* EoRR request.
*/
if (CHECK_FLAG(
peer->af_sflags[afi][safi],
PEER_STATUS_BORR_SEND)) {
bgp_route_refresh_send(
peer, afi, safi, 0, 0,
0,
BGP_ROUTE_REFRESH_EORR);
SET_FLAG(peer->af_sflags[afi]
[safi],
PEER_STATUS_EORR_SEND);
UNSET_FLAG(
peer->af_sflags[afi]
[safi],
PEER_STATUS_BORR_SEND);
if (bgp_debug_neighbor_events(
peer))
zlog_debug(
"%pBP sending route-refresh (EoRR) for %s/%s",
peer,
afi2str(afi),
safi2str(safi));
}
}
if (CHECK_FLAG(peer->cap,
PEER_CAP_RESTART_RCV)) {
if (!(PAF_SUBGRP(paf))->t_coalesce
&& peer->afc_nego[afi][safi]
&& peer->synctime
&& !CHECK_FLAG(
peer->af_sflags[afi][safi],
PEER_STATUS_EOR_SEND)) {
/* If EOR is disabled,
* the message is not sent
*/
if (BGP_SEND_EOR(peer->bgp, afi,
safi)) {
SET_FLAG(
peer->af_sflags
[afi]
[safi],
PEER_STATUS_EOR_SEND);
/* Update EOR
* send time
*/
peer->eor_stime[afi]
[safi] =
monotime(NULL);
BGP_UPDATE_EOR_PKT(
peer, afi, safi,
s);
bgp_process_pending_refresh(
peer, afi,
safi);
}
}
}
continue;
}
/* Update packet send time */
peer->pkt_stime[afi][safi] = monotime(NULL);
/* Found a packet template to send, overwrite
* packet with appropriate attributes from peer
* and advance peer */
s = bpacket_reformat_for_peer(next_pkt, paf);
bgp_packet_add(peer, s);
bpacket_queue_advance_peer(paf);
}
} while (s && (++generated < wpq) &&
(peer->obuf->count <= bm->outq_limit));
if (generated)
bgp_writes_on(peer);
bgp_write_proceed_actions(peer);
}
|
到此我们分析了接受到UPDATE消息,然后在BGP 路由表里面添加了路由,并且发送出去的全部过程,涉及的路径很长,细节很大,只有后面再慢慢体会。
本文参考
- BGP官方文档
- FRR BGP 协议分析