FRR BGP源码分析3 -- FSM 状态机
前面创建完bgp peer之后,peer是active的话就会开启bgp_start_timer,然后开始BGP状态机的协商。
状态机简介
下面是BGP的状态和事件驱动的定义:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
/*
* BGP finite state machine events
*
* Note: these do not correspond to RFC-defined event codes. Those are
* defined elsewhere.
*/
enum bgp_fsm_events {
BGP_Start = 1,
BGP_Stop,
TCP_connection_open,
TCP_connection_open_w_delay,
TCP_connection_closed,
TCP_connection_open_failed,
TCP_fatal_error,
ConnectRetry_timer_expired,
Hold_Timer_expired,
KeepAlive_timer_expired,
DelayOpen_timer_expired,
Receive_OPEN_message,
Receive_KEEPALIVE_message,
Receive_UPDATE_message,
Receive_NOTIFICATION_message,
Clearing_Completed,
BGP_EVENTS_MAX,
};
/* BGP finite state machine status. */
enum bgp_fsm_status {
Idle = 1,
Connect,
Active,
OpenSent,
OpenConfirm,
Established,
Clearing,
Deleted,
BGP_STATUS_MAX,
};
bgp是基于tcp协议的,即包含了tcp协议的优点,因此上面的状态机也就跟tcp连接有一定的关系:
- tcp连接建立阶段的状态: Idle , Connect , Active
- tcp连接建立完成之后: OpenSent , OpenConfirm , Established
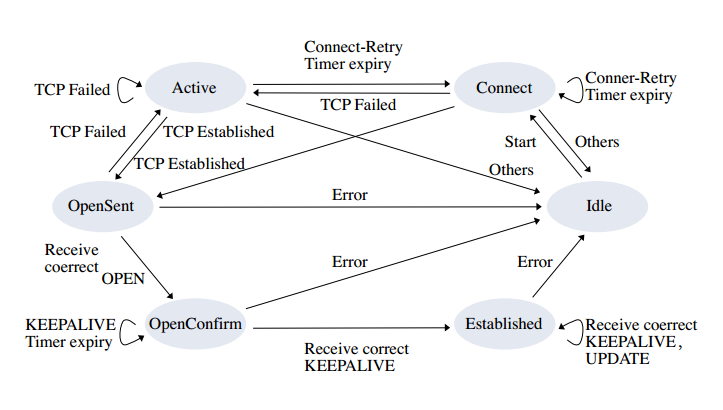
Idle
BGP协议初始时是处于Idle状态。在这个状态时,系统不分配任何资源,也拒绝所有进入的BGP连接。只有收到 Start Event 时,才分配BGP资源,启动ConnectRetry计时器,启动对其它BGP对等体的传输层连接,同时也侦听是否有来自其它对等体的连接请求。
Connect
这个状态下,BGP等待TCP完成连接。若连接成功,本地清空ConnectRetry计时器,并向对等体发送OPEN报文,然后状态改变为OpenSent状态;否则,本地重置ConnectRetry计时器,侦听是否有对等体启动连接, 并移至Active状态。
Active
这个状态下,BGP初始化TCP连接来获得一个对等体。如果连接成功,本地清空ConnectRetry计时器,并向对等体发送OPEN报文,并转至OpenSent状态。
OpenSent
这个状态下,BGP等待对等体的OPEN报文。收到报文后对报文进行检查,如果发现错误,本地发送NOTIFICATION报文给对等体,并改变状态为IDLE。如果报文正确,BGP发送KEEPALIVE报文,并转至OpenConfirm状态。
OpenConfirm
这个状态下,BGP等待KEEPALIVE或NOTIFICATION报文。如果收到KEEPALIVE报文,则进入Established状态,如果收到NOTIFICATION报文,则变为Idle状态。
Established
这个状态下,BGP可以和其他对等体交换UPDATE,NOTIFICATION,KEEPALIVE报文。如果收到了正确的UPDATE或KEEPALIVE报文,就认为对端处于正常运行状态, 本地重置Hold Timer。如果收到NOTIFICATION报文,本地转到Idle状态。如果收到错误的UPDATE报文,本地发送NOTIFICATION报文通知对端,并改变本地状态为Idle。 如果收到了TCP拆链通知,本地关闭BGP连接,并回到Idle状态。
综上, 我们可以画出BGP的有限状态机:
BGP的FSM代码写的相当漂亮,使用 当前状态 + EVENT 作为FSM index,查找到对应的执行函数和下一个状态,FSM结构如下,用于处理BGP协议中对等体的状态转换:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
/* Finite State Machine structure */
static const struct {
enum bgp_fsm_state_progress (*func)(struct peer *); //处理特定事件的函数的指针
enum bgp_fsm_status next_state; //指定在处理完特定事件后,对等体应该转移到的下一个状态
} FSM[BGP_STATUS_MAX - 1][BGP_EVENTS_MAX - 1] = {
{
/* Idle state: In Idle state, all events other than BGP_Start is
ignored. With BGP_Start event, finite state machine calls
bgp_start(). */
{bgp_start, Connect}, /* BGP_Start */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* BGP_Stop */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* TCP_connection_open */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* TCP_connection_open_w_delay */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* TCP_connection_closed */
{bgp_ignore, Idle}, /* TCP_connection_open_failed */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* TCP_fatal_error */
{bgp_ignore, Idle}, /* ConnectRetry_timer_expired */
{bgp_ignore, Idle}, /* Hold_Timer_expired */
{bgp_ignore, Idle}, /* KeepAlive_timer_expired */
{bgp_ignore, Idle}, /* DelayOpen_timer_expired */
{bgp_ignore, Idle}, /* Receive_OPEN_message */
{bgp_ignore, Idle}, /* Receive_KEEPALIVE_message */
{bgp_ignore, Idle}, /* Receive_UPDATE_message */
{bgp_ignore, Idle}, /* Receive_NOTIFICATION_message */
{bgp_ignore, Idle}, /* Clearing_Completed */
},
{
/* Connect */
{bgp_ignore, Connect}, /* BGP_Start */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* BGP_Stop */
{bgp_connect_success, OpenSent}, /* TCP_connection_open */
{bgp_connect_success_w_delayopen,
Connect}, /* TCP_connection_open_w_delay */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* TCP_connection_closed */
通过FSM二维数组,bgp_event_update接收一个对等体和一个BGP有限状态机事件作为参数,然后根据当前状态和事件执行相应的状态转换和处理,让状态机转化的代码起到了化繁为简的神奇效果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
int bgp_event_update(struct peer *peer, enum bgp_fsm_events event)
{
enum bgp_fsm_status next;
enum bgp_fsm_state_progress ret = 0;
struct peer *other;
int passive_conn = 0;
int dyn_nbr;
/* default return code */
ret = FSM_PEER_NOOP;
other = peer->doppelganger;
passive_conn =
(CHECK_FLAG(peer->sflags, PEER_STATUS_ACCEPT_PEER)) ? 1 : 0;
dyn_nbr = peer_dynamic_neighbor(peer);
/* Logging this event. */
next = FSM[peer->status - 1][event - 1].next_state;
if (bgp_debug_neighbor_events(peer) && peer->status != next)
zlog_debug("%s [FSM] %s (%s->%s), fd %d", peer->host,
bgp_event_str[event],
lookup_msg(bgp_status_msg, peer->status, NULL),
lookup_msg(bgp_status_msg, next, NULL), peer->fd);
peer->last_event = peer->cur_event;
peer->cur_event = event;
/* Call function. */
if (FSM[peer->status - 1][event - 1].func)
ret = (*(FSM[peer->status - 1][event - 1].func))(peer);
状态机转化
Peer初始状态是IDLE,那么对等体一旦start起来,就会进入各自的状态,在不同的状态下处理各自的事件消息。
IDLE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
/* BGP start timer. This function set BGP_Start event to thread value
and process event. */
static void bgp_start_timer(struct event *thread)
{
struct peer *peer;
peer = EVENT_ARG(thread);
if (bgp_debug_neighbor_events(peer))
zlog_debug("%s [FSM] Timer (start timer expire).", peer->host);
EVENT_VAL(thread) = BGP_Start;
bgp_event(thread); /* bgp_event unlocks peer */
}
bgp_event将调用bgp_event_update进行event处理和状态更新
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
/* Execute event process. */
void bgp_event(struct event *thread)
{
enum bgp_fsm_events event;
struct peer *peer;
peer = EVENT_ARG(thread);
event = EVENT_VAL(thread);
peer_lock(peer);
bgp_event_update(peer, event);
peer_unlock(peer);
}
start定时器到期后, EVNET 为 BGP_Start,在bgp_event_update函数里面,通过FSM的数组获取
func = bgp_start
next_state = Connect
bgp_start
尝试使用非阻塞IO连接到远程对等体,并检查连接信息:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
/* This function is the first starting point of all BGP connection. It
* try to connect to remote peer with non-blocking IO.
*/
enum bgp_fsm_state_progress bgp_start(struct peer *peer)
{
int status;
bgp_peer_conf_if_to_su_update(peer);
if (peer->su.sa.sa_family == AF_UNSPEC) {
if (bgp_debug_neighbor_events(peer))
zlog_debug(
"%s [FSM] Unable to get neighbor's IP address, waiting...",
peer->host);
peer->last_reset = PEER_DOWN_NBR_ADDR;
return BGP_FSM_FAILURE;
}
bgp_connect
之后调用 bgp_connect 创建并配置用于连接的套接字,开始建立TCP的连接,bgp使用tcp连接,每个bgp实例自身是peer的一个tcp server端,同时也是peer的tcp client端,server端在bgp_create之后都建立自己的socket服务端开始监听179端口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
/* BGP try to connect to the peer. */
int bgp_connect(struct peer *peer)
{
assert(!CHECK_FLAG(peer->thread_flags, PEER_THREAD_WRITES_ON));
assert(!CHECK_FLAG(peer->thread_flags, PEER_THREAD_READS_ON));
ifindex_t ifindex = 0;
if (peer->conf_if && BGP_PEER_SU_UNSPEC(peer)) {
if (bgp_debug_neighbor_events(peer))
zlog_debug("Peer address not learnt: Returning from connect");
return 0;
}
frr_with_privs(&bgpd_privs) {
/* Make socket for the peer. */
peer->fd = vrf_sockunion_socket(&peer->su, peer->bgp->vrf_id,
bgp_get_bound_name(peer));
}
peer->fd = vrf_sockunion_socket该命令创建连接peer的客服端的TCP fd,同时设置FD为非阻塞,因为FRR是事件驱动,不能由于fd阻塞导致线程给挂起。- 如果配置了密码会添加TCP MD5签名验证选项,在服务端,直接由内核在tcp接收处理时就完成了签名验证。
- 更新TCP连接的源IP地址
1
2
3
4
5
/* Update source bind. */
if (bgp_update_source(peer) < 0) {
peer->last_reset = PEER_DOWN_SOCKET_ERROR;
return connect_error;
}
然后调用 bgp_update_source 通过 sockunion_bind 绑定配置的源IP地址
最后调用sockunion_connect尝试与远程对等体建立连接
至此套接字创建、选项设置和连接的发起都已完成,进入 Connect 状态
Connect 处理
调用sockunion_connect处理非阻塞connect到服务端,返回连接的状态,包括连接成功、连接进行中或连接错误
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
/* Performs a non-blocking connect(). */
enum connect_result sockunion_connect(int fd, const union sockunion *peersu,
unsigned short port, ifindex_t ifindex)
{
int ret;
union sockunion su;
memcpy(&su, peersu, sizeof(union sockunion));
switch (su.sa.sa_family) {
case AF_INET:
su.sin.sin_port = port;
break;
case AF_INET6:
su.sin6.sin6_port = port;
#ifdef KAME
if (IN6_IS_ADDR_LINKLOCAL(&su.sin6.sin6_addr) && ifindex) {
su.sin6.sin6_scope_id = ifindex;
SET_IN6_LINKLOCAL_IFINDEX(su.sin6.sin6_addr, ifindex);
}
#endif /* KAME */
break;
}
/* Call connect function. */
ret = connect(fd, (struct sockaddr *)&su, sockunion_sizeof(&su));
/* Immediate success */
if (ret == 0)
return connect_success;
/* If connect is in progress then return 1 else it's real error. */
if (ret < 0) {
if (errno != EINPROGRESS) {
char str[SU_ADDRSTRLEN];
zlog_info("can't connect to %s fd %d : %s",
sockunion_log(&su, str, sizeof(str)), fd,
safe_strerror(errno));
return connect_error;
}
}
return connect_in_progress; //表示连接正在进行中
}
由于 fd 是no block(非阻塞)的,所以调用connect触发TCP的三次握手,连接不能立即完成(如果是阻塞的话,线程会被挂住),按照connect的man帮助,返回值如下,查看解释,可以理解代码的返回值处理:
RETURN VALUE
If the connection or binding succeeds, zero is returned. On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately.
EINPROGRESS
The socket is nonblocking and the connection cannot be completed immediately. It is possible to select(2) or poll(2) for completion by selecting the socket for writing. After select(2) indicates writability, use getsock‐opt(2) to read the SO_ERROR option at level SOL_SOCKET to determine whether connect() completed successfully (SO_ERROR is zero) or unsuccessfully (SO_ERROR is one of the usual error codes listed here, explaining the reason for the failure).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
status = bgp_connect(peer);
switch (status) {
case connect_error:
if (bgp_debug_neighbor_events(peer))
zlog_debug("%s [FSM] Connect error", peer->host);
BGP_EVENT_ADD(peer, TCP_connection_open_failed);
break;
case connect_success:
if (bgp_debug_neighbor_events(peer))
zlog_debug(
"%s [FSM] Connect immediately success, fd %d",
peer->host, peer->fd);
BGP_EVENT_ADD(peer, TCP_connection_open);
break;
case connect_in_progress:
/* To check nonblocking connect, we wait until socket is
readable or writable. */
if (bgp_debug_neighbor_events(peer))
zlog_debug(
"%s [FSM] Non blocking connect waiting result, fd %d",
peer->host, peer->fd);
if (peer->fd < 0) {
flog_err(EC_BGP_FSM,
"%s peer's fd is negative value %d", __func__,
peer->fd);
return BGP_FSM_FAILURE;
}
/*
* - when the socket becomes ready, poll() will signify POLLOUT
* - if it fails to connect, poll() will signify POLLHUP
* - POLLHUP is handled as a 'read' event by thread.c
*
* therefore, we schedule both a read and a write event with
* bgp_connect_check() as the handler for each and cancel the
* unused event in that function.
*/
event_add_read(bm->master, bgp_connect_check, peer, peer->fd,
&peer->t_connect_check_r);
event_add_write(bm->master, bgp_connect_check, peer, peer->fd,
&peer->t_connect_check_w);
break;
}
所以当bgp_connect返回的时候,根据返回值的不同会做不同的处理:
- connect_success:触发
TCP_connection_open事件BGP_EVENT_ADD(peer, TCP_connection_open); - connect_in_progress:说明connect并没有成功,会触发fd的可读和可写的事件(根据前面man的说明可以理解这点),
bgp_connect_check回调函数根据getsockopt(peer->fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_ERROR, (void *)&status, &slen);来判断connect链接是否OK。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
/**
* Determines whether a TCP session has successfully established for a peer and
* events as appropriate.
*
* This function is called when setting up a new session. After connect() is
* called on the peer's socket (in bgp_start()), the fd is passed to poll()
* to wait for connection success or failure. When poll() returns, this
* function is called to evaluate the result.
*
* Due to differences in behavior of poll() on Linux and BSD - specifically,
* the value of .revents in the case of a closed connection - this function is
* scheduled both for a read and a write event. The write event is triggered
* when the connection is established. A read event is triggered when the
* connection is closed. Thus we need to cancel whichever one did not occur.
*/
static void bgp_connect_check(struct event *thread)
{
int status;
socklen_t slen;
int ret;
struct peer *peer;
peer = EVENT_ARG(thread);
assert(!CHECK_FLAG(peer->thread_flags, PEER_THREAD_READS_ON));
assert(!CHECK_FLAG(peer->thread_flags, PEER_THREAD_WRITES_ON));
assert(!peer->t_read);
assert(!peer->t_write);
EVENT_OFF(peer->t_connect_check_r);
EVENT_OFF(peer->t_connect_check_w);
/* Check file descriptor. */
slen = sizeof(status);
ret = getsockopt(peer->fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_ERROR, (void *)&status,
&slen);
/* If getsockopt is fail, this is fatal error. */
if (ret < 0) {
zlog_err("can't get sockopt for nonblocking connect: %d(%s)",
errno, safe_strerror(errno));
BGP_EVENT_ADD(peer, TCP_fatal_error);
return;
}
/* When status is 0 then TCP connection is established. */
if (status == 0) {
if (CHECK_FLAG(peer->flags, PEER_FLAG_TIMER_DELAYOPEN))
BGP_EVENT_ADD(peer, TCP_connection_open_w_delay);
else
BGP_EVENT_ADD(peer, TCP_connection_open);
return;
} else {
if (bgp_debug_neighbor_events(peer))
zlog_debug("%s [Event] Connect failed %d(%s)",
peer->host, status, safe_strerror(status));
BGP_EVENT_ADD(peer, TCP_connection_open_failed);
return;
}
}
然后函数直接返回,最后达到bgp_event_update,会把peer的状态改成Connect (connect触发TCP链接不是立马成功的情况下)
Connect
当调用connect触发TCP的三次握手的时候,connect没有阻塞而是直接返回了,然后添加了FD可读和可写的事件,回调函数是bgp_connect_check函数,然后调用getsockopt 获取TCP connection的情况,如果status返回的是0,那么说明TCP connection is established,然后触发 TCP_connection_open事件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
/* When status is 0 then TCP connection is established. */
if (status == 0) {
if (CHECK_FLAG(peer->flags, PEER_FLAG_TIMER_DELAYOPEN))
BGP_EVENT_ADD(peer, TCP_connection_open_w_delay);
else
BGP_EVENT_ADD(peer, TCP_connection_open);
return;
} else {
if (bgp_debug_neighbor_events(peer))
zlog_debug("%s [Event] Connect failed %d(%s)",
peer->host, status, safe_strerror(status));
BGP_EVENT_ADD(peer, TCP_connection_open_failed);
return;
}
而此时peer的状态是connect,根据全局的FSM可以知道,下一状态是OpenSent:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
{
/* Connect */
{bgp_ignore, Connect}, /* BGP_Start */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* BGP_Stop */
{bgp_connect_success, OpenSent}, /* TCP_connection_open */
{bgp_connect_success_w_delayopen,
Connect}, /* TCP_connection_open_w_delay */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* TCP_connection_closed */
{bgp_connect_fail, Active}, /* TCP_connection_open_failed */
{bgp_connect_fail, Idle}, /* TCP_fatal_error */
{bgp_reconnect, Connect}, /* ConnectRetry_timer_expired */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* Hold_Timer_expired */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* KeepAlive_timer_expired */
{bgp_fsm_delayopen_timer_expire,
OpenSent}, /* DelayOpen_timer_expired */
{bgp_fsm_open, OpenConfirm}, /* Receive_OPEN_message */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* Receive_KEEPALIVE_message */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* Receive_UPDATE_message */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* Receive_NOTIFICATION_message */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* Clearing_Completed */
},
OpenSent
回调函数:bgp_connect_success
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
/* TCP connection open. Next we send open message to remote peer. And
add read thread for reading open message. */
static enum bgp_fsm_state_progress bgp_connect_success(struct peer *peer)
{
if (peer->fd < 0) {
flog_err(EC_BGP_CONNECT, "%s peer's fd is negative value %d",
__func__, peer->fd);
return bgp_stop(peer);
}
if (bgp_getsockname(peer) < 0) { //获取本地套接字的地址信息,并检查
flog_err_sys(EC_LIB_SOCKET,
"%s: bgp_getsockname(): failed for peer %s, fd %d",
__func__, peer->host, peer->fd);
bgp_notify_send(peer, BGP_NOTIFY_FSM_ERR,
bgp_fsm_error_subcode(peer->status));
bgp_writes_on(peer);
return BGP_FSM_FAILURE;
}
/*
* If we are doing nht for a peer that ls v6 LL based
* massage the event system to make things happy
*/
bgp_nht_interface_events(peer);
bgp_reads_on(peer);
if (bgp_debug_neighbor_events(peer)) {
if (!CHECK_FLAG(peer->sflags, PEER_STATUS_ACCEPT_PEER))
zlog_debug("%s open active, local address %pSU",
peer->host, peer->su_local);
else
zlog_debug("%s passive open", peer->host);
}
/* Send an open message */
bgp_open_send(peer);
return BGP_FSM_SUCCESS;
}
bgp_connect_success 主要完成:
- 开启IO线程对peer fd的可读事件,当对端发送消息到peer的时候,IO线程就会被唤醒,调用回调函数
bgp_process_reads处理报文
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
void bgp_reads_on(struct peer *peer)
{
struct frr_pthread *fpt = bgp_pth_io;
assert(fpt->running);
assert(peer->status != Deleted);
assert(peer->ibuf);
assert(peer->fd);
assert(peer->ibuf_work);
assert(peer->obuf);
assert(!peer->t_connect_check_r);
assert(!peer->t_connect_check_w);
assert(peer->fd);
event_add_read(fpt->master, bgp_process_reads, peer, peer->fd,
&peer->t_read);
SET_FLAG(peer->thread_flags, PEER_THREAD_READS_ON);
}
- 构造OPEN 报文,并开启IO线程对peer fd的可写事件,当本端发送消息到peer的时候,IO线程就会被唤醒,调用回调函数
bgp_process_writes处理报文
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
/*
* Creates a BGP Open packet and appends it to the peer's output queue.
* Sets capabilities as necessary.
*/
void bgp_open_send(struct peer *peer)
{
struct stream *s;
uint16_t send_holdtime;
as_t local_as;
if (CHECK_FLAG(peer->flags, PEER_FLAG_TIMER))
send_holdtime = peer->holdtime;
else
send_holdtime = peer->bgp->default_holdtime;
/* local-as Change */
if (peer->change_local_as)
local_as = peer->change_local_as;
else
local_as = peer->local_as;
s = stream_new(BGP_STANDARD_MESSAGE_MAX_PACKET_SIZE);
/* Make open packet. */
bgp_packet_set_marker(s, BGP_MSG_OPEN);
/* Set open packet values. */
stream_putc(s, BGP_VERSION_4); /* BGP version */
stream_putw(s, (local_as <= BGP_AS_MAX) ? (uint16_t)local_as
: BGP_AS_TRANS);
stream_putw(s, send_holdtime); /* Hold Time */
stream_put_in_addr(s, &peer->local_id); /* BGP Identifier */
/* Set capabilities */
if (CHECK_FLAG(peer->flags, PEER_FLAG_EXTENDED_OPT_PARAMS)) {
(void)bgp_open_capability(s, peer, true);
} else {
struct stream *tmp = stream_new(STREAM_SIZE(s));
stream_copy(tmp, s);
if (bgp_open_capability(tmp, peer, false)
> BGP_OPEN_NON_EXT_OPT_LEN) {
stream_free(tmp);
(void)bgp_open_capability(s, peer, true);
} else {
stream_copy(s, tmp);
stream_free(tmp);
}
}
/* Set BGP packet length. */
bgp_packet_set_size(s);
if (bgp_debug_neighbor_events(peer))
zlog_debug(
"%s sending OPEN, version %d, my as %u, holdtime %d, id %pI4",
peer->host, BGP_VERSION_4, local_as, send_holdtime,
&peer->local_id);
/* Dump packet if debug option is set. */
/* bgp_packet_dump (s); */
hook_call(bgp_packet_send, peer, BGP_MSG_OPEN, stream_get_endp(s), s);
/* Add packet to the peer. */
bgp_packet_add(peer, s);
bgp_writes_on(peer);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
void bgp_writes_on(struct peer *peer)
{
struct frr_pthread *fpt = bgp_pth_io;
assert(fpt->running);
assert(peer->status != Deleted);
assert(peer->obuf);
assert(peer->ibuf);
assert(peer->ibuf_work);
assert(!peer->t_connect_check_r);
assert(!peer->t_connect_check_w);
assert(peer->fd);
event_add_write(fpt->master, bgp_process_writes, peer, peer->fd,
&peer->t_write);
SET_FLAG(peer->thread_flags, PEER_THREAD_WRITES_ON);
}
IO线程被唤醒,执行bgp_process_writes,然后调用bgp_write 把OPEN消息发送到对端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
/*
* Called from I/O pthread when a file descriptor has become ready for writing.
*/
static void bgp_process_writes(struct event *thread)
{
static struct peer *peer;
peer = EVENT_ARG(thread);
uint16_t status;
bool reschedule;
bool fatal = false;
if (peer->fd < 0)
return;
struct frr_pthread *fpt = bgp_pth_io;
frr_with_mutex (&peer->io_mtx) {
status = bgp_write(peer);
reschedule = (stream_fifo_head(peer->obuf) != NULL);
}
当函数返回到bgp_event_update,会把peer的状态改成OpenSend
OpenSend
IO线程此时睡眠,等待对端OPEN报文的到来,当收到报文后,IO线程就会被唤醒,调用回调函数bgp_process_reads处理报文
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
/*
* Called from I/O pthread when a file descriptor has become ready for reading,
* or has hung up.
*
* We read as much data as possible, process as many packets as we can and
* place them on peer->ibuf for secondary processing by the main thread.
*/
while (true) {
ret = read_ibuf_work(peer);
if (ret <= 0)
break;
added_pkt = true;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
/*
* If we have that much data, chuck it into its own
* stream and append to input queue for processing.
*
* Otherwise, come back later.
*/
if (ringbuf_remain(ibw) < pktsize)
return 0;
pkt = stream_new(pktsize);
assert(STREAM_WRITEABLE(pkt) == pktsize);
assert(ringbuf_get(ibw, pkt->data, pktsize) == pktsize);
stream_set_endp(pkt, pktsize);
frrtrace(2, frr_bgp, packet_read, peer, pkt);
frr_with_mutex (&peer->io_mtx) {
stream_fifo_push(peer->ibuf, pkt);
}
如果读取到了报文,那么放入peer的struct stream_fifo *ibuf; (packets waiting to be processed) 里面,唤醒主线程取报文处理,主线程回调处理函数为bgp_process_packet
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
/* handle invalid header */
if (fatal) {
/* wipe buffer just in case someone screwed up */
ringbuf_wipe(peer->ibuf_work);
return;
}
event_add_read(fpt->master, bgp_process_reads, peer, peer->fd,
&peer->t_read);
if (added_pkt)
event_add_event(bm->master, bgp_process_packet, peer, 0,
&peer->t_process_packet);
主线程唤醒执行bgp_process_packet 处理ibuf的报文,然后根据解析出来的BGP 报文类型,走不同的处理逻辑,本次我们关心的接受到OPEN的消息的处理,处理函数是bgp_open_receive
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
/* Read rest of the packet and call each sort of packet routine
*/
switch (type) {
case BGP_MSG_OPEN:
frrtrace(2, frr_bgp, open_process, peer, size);
atomic_fetch_add_explicit(&peer->open_in, 1,
memory_order_relaxed);
mprc = bgp_open_receive(peer, size);
if (mprc == BGP_Stop)
flog_err(
EC_BGP_PKT_OPEN,
"%s: BGP OPEN receipt failed for peer: %s",
__func__, peer->host);
break;
case BGP_MSG_UPDATE:
frrtrace(2, frr_bgp, update_process, peer, size);
atomic_fetch_add_explicit(&peer->update_in, 1,
memory_order_relaxed);
peer->readtime = monotime(NULL);
mprc = bgp_update_receive(peer, size);
if (mprc == BGP_Stop)
flog_err(
EC_BGP_UPDATE_RCV,
"%s: BGP UPDATE receipt failed for peer: %s",
__func__, peer->host);
break;
bgp_open_receive处理 OPEN 报文包含各种能力值的验证,如果存在差错,则返回BGP_stop 事件,后续会发送Notification消息,并把状态迁移到IDLE状态,如果没有差错,则返回Receive_OPEN_message 事件,然后根据返回的事件处理状态机mprc的值本次就是Receive_OPEN_message
1
2
3
4
5
/* Update FSM */
if (mprc != BGP_PACKET_NOOP)
fsm_update_result = bgp_event_update(peer, mprc);
else
continue;
根据FSM数组可以定位到,收到OPEN消息后的处理,下一个状态是OpenConfirm,处理函数是:bgp_fsm_open
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
{
/* OpenSent, */
{bgp_ignore, OpenSent}, /* BGP_Start */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* BGP_Stop */
{bgp_stop, Active}, /* TCP_connection_open */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* TCP_connection_open_w_delay */
{bgp_stop, Active}, /* TCP_connection_closed */
{bgp_stop, Active}, /* TCP_connection_open_failed */
{bgp_stop, Active}, /* TCP_fatal_error */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* ConnectRetry_timer_expired */
{bgp_fsm_holdtime_expire, Idle}, /* Hold_Timer_expired */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* KeepAlive_timer_expired */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* DelayOpen_timer_expired */
{bgp_fsm_open, OpenConfirm}, /* Receive_OPEN_message */
{bgp_fsm_event_error, Idle}, /* Receive_KEEPALIVE_message */
{bgp_fsm_event_error, Idle}, /* Receive_UPDATE_message */
{bgp_fsm_event_error, Idle}, /* Receive_NOTIFICATION_message */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* Clearing_Completed */
},
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
static enum bgp_fsm_state_progress bgp_fsm_open(struct peer *peer)
{
/* If DelayOpen is active, we may still need to send an open message */
if ((peer->status == Connect) || (peer->status == Active))
bgp_open_send(peer);
/* Send keepalive and make keepalive timer */
bgp_keepalive_send(peer);
return BGP_FSM_SUCCESS;
}
发送keeplive消息后,状态机转化为OpenConfirm
OpenConfirm
前面IO线程处理和bgp_process_packet处理都一样,只是此时OpenConfirm等待Keeplive或者Notification消息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
case BGP_MSG_KEEPALIVE:
frrtrace(2, frr_bgp, keepalive_process, peer, size);
peer->readtime = monotime(NULL);
atomic_fetch_add_explicit(&peer->keepalive_in, 1,
memory_order_relaxed);
mprc = bgp_keepalive_receive(peer, size);
if (mprc == BGP_Stop)
flog_err(
EC_BGP_KEEP_RCV,
"%s: BGP KEEPALIVE receipt failed for peer: %s",
__func__, peer->host);
break;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
/**
* Process BGP KEEPALIVE message for peer.
*
* @param peer
* @param size size of the packet
* @return as in summary
*/
static int bgp_keepalive_receive(struct peer *peer, bgp_size_t size)
{
if (bgp_debug_keepalive(peer))
zlog_debug("%s KEEPALIVE rcvd", peer->host);
bgp_update_implicit_eors(peer);
peer->rtt = sockopt_tcp_rtt(peer->fd);
/* If the peer's RTT is higher than expected, shutdown
* the peer automatically.
*/
if (!CHECK_FLAG(peer->flags, PEER_FLAG_RTT_SHUTDOWN))
return Receive_KEEPALIVE_message;
if (peer->rtt > peer->rtt_expected) {
peer->rtt_keepalive_rcv++;
if (peer->rtt_keepalive_rcv > peer->rtt_keepalive_conf) {
char rtt_shutdown_reason[BUFSIZ] = {};
snprintfrr(
rtt_shutdown_reason,
sizeof(rtt_shutdown_reason),
"shutdown due to high round-trip-time (%dms > %dms, hit %u times)",
peer->rtt, peer->rtt_expected,
peer->rtt_keepalive_rcv);
zlog_warn("%s %s", peer->host, rtt_shutdown_reason);
SET_FLAG(peer->sflags, PEER_STATUS_RTT_SHUTDOWN);
peer_tx_shutdown_message_set(peer, rtt_shutdown_reason);
peer_flag_set(peer, PEER_FLAG_SHUTDOWN);
}
} else {
if (peer->rtt_keepalive_rcv)
peer->rtt_keepalive_rcv--;
}
return Receive_KEEPALIVE_message;
}
事件是Receive_KEEPALIVE_message,根据FSM数组可以定位到,收到Keeplive消息后的处理,下一个状态是Established,处理函数是:bgp_establish
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
{
/* OpenConfirm, */
{bgp_ignore, OpenConfirm}, /* BGP_Start */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* BGP_Stop */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* TCP_connection_open */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* TCP_connection_open_w_delay */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* TCP_connection_closed */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* TCP_connection_open_failed */
{bgp_stop, Idle}, /* TCP_fatal_error */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* ConnectRetry_timer_expired */
{bgp_fsm_holdtime_expire, Idle}, /* Hold_Timer_expired */
{bgp_ignore, OpenConfirm}, /* KeepAlive_timer_expired */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* DelayOpen_timer_expired */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* Receive_OPEN_message */
{bgp_establish, Established}, /* Receive_KEEPALIVE_message */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* Receive_UPDATE_message */
{bgp_stop_with_error, Idle}, /* Receive_NOTIFICATION_message */
{bgp_fsm_exception, Idle}, /* Clearing_Completed */
},
Established
bgp_establish 会处理标志重置、更新哈希表、路由更新等:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
/**
* Transition to Established state.
*
* Convert peer from stub to full fledged peer, set some timers, and generate
* initial updates.
*/
static enum bgp_fsm_state_progress bgp_establish(struct peer *peer)
{
afi_t afi;
safi_t safi;
int nsf_af_count = 0;
enum bgp_fsm_state_progress ret = BGP_FSM_SUCCESS;
struct peer *other;
int status;
struct peer *orig = peer;
other = peer->doppelganger;
hash_release(peer->bgp->peerhash, peer);
if (other)
hash_release(peer->bgp->peerhash, other);
本文参考